Runtime Performance Comparison¶
Because Sorted Containers is implemented in pure-Python, its performance depends directly on the Python runtime. Sorted Containers is primarily developed, tested and benchmarked on CPython 3.7.
Not all runtimes are created equal. The graphs below compare Sorted Containers running on the CPython 3.7, CPython 2.7, and PyPy runtimes. As of Python 3.7 the CPython 3.7 runtime is now faster than the CPython 2.7 runtime. The PyPy runtime displays much more variability due to its JIT-ed nature. Once the just-in-time compiler optimizes the code, performance is often two to ten times faster.
Performance of competing implementations are benchmarked against the CPython 3.7 runtime. An implementation performance comparison is also included with data from popular sorted container packages.
Sorted Containers uses a segmented-list data structure similar to a B-tree limited to two levels of nodes. As part of the implementation, a load factor is used to determine how many values should be stored in each node. This can have a significant impact on performance and a load factor performance comparison is also provided.
Though these benchmarks exercise only one API repeatedly, an effort has also been made to simulate real-world workloads. The simulated workload performance comparison contains examples with comparisons to other implementations, load factors, and runtimes.
Sorted List¶
Graphs comparing Sorted List performance.
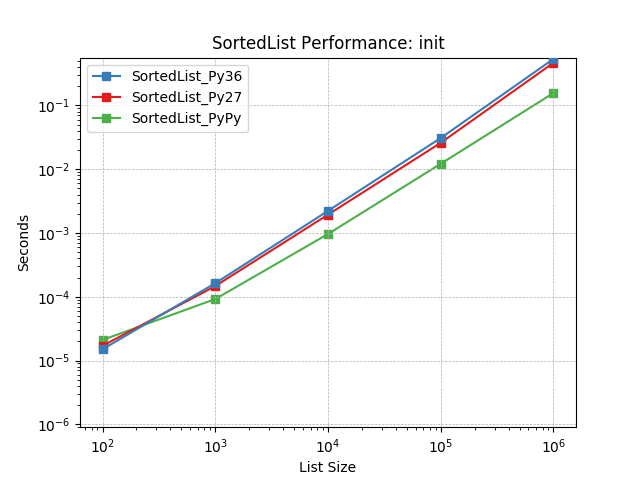
__init__¶
Initializing with a list of random numbers using SortedList.__init__().
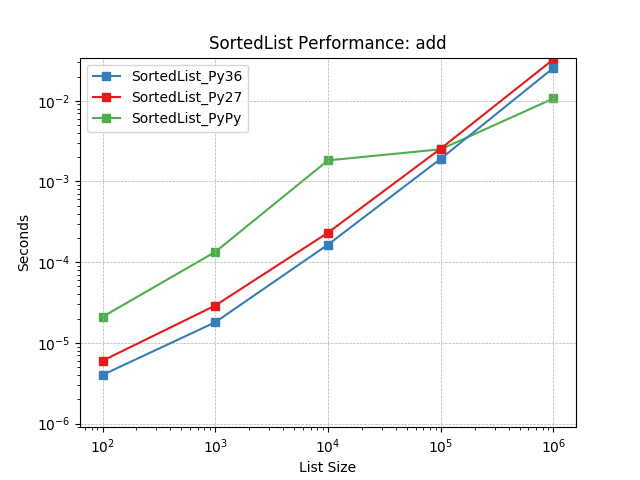
add¶
Randomly adding values using SortedList.add().
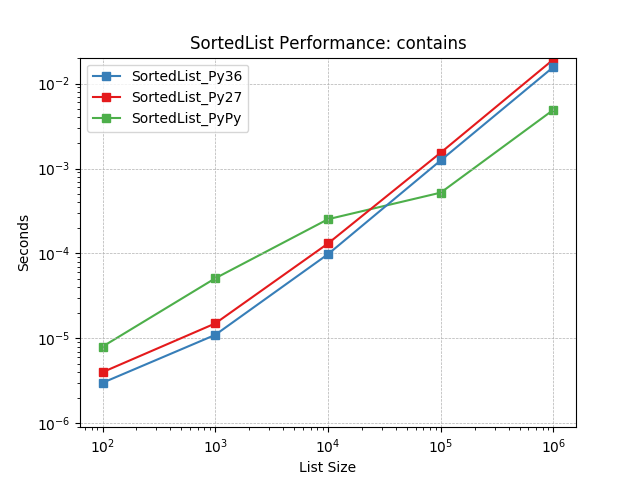
contains¶
Randomly testing membership using SortedList.__contains__().
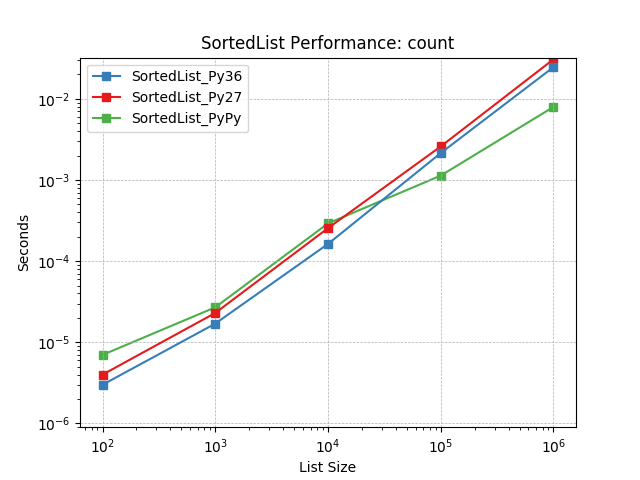
count¶
Counting objects at random using SortedList.count().
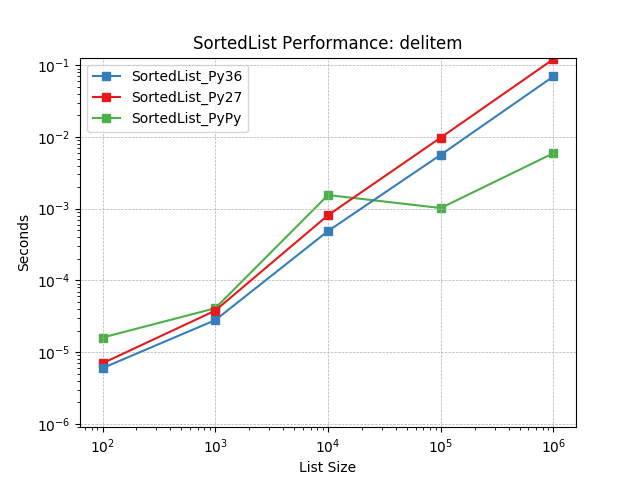
__delitem__¶
Deleting objects at random using SortedList.__delitem__().
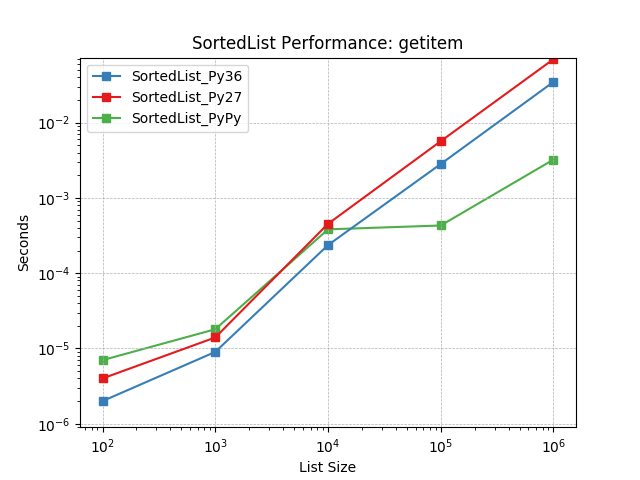
__getitem__¶
Retrieving objects by index using SortedList.__getitem__().
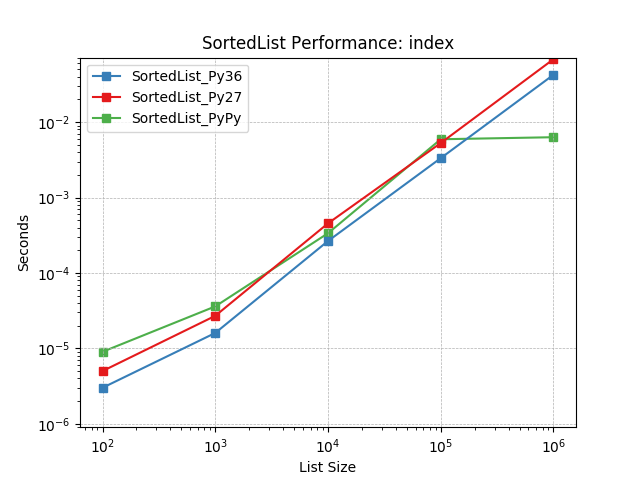
index¶
Finding the index of an object using SortedList.index().
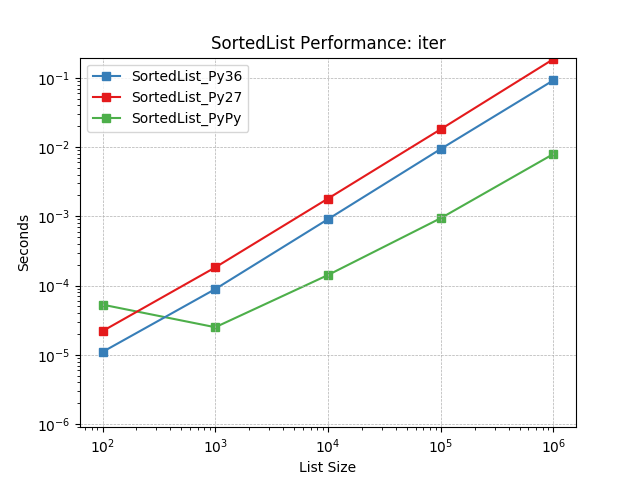
iter¶
Iterating a SortedList using SortedList.__iter__().
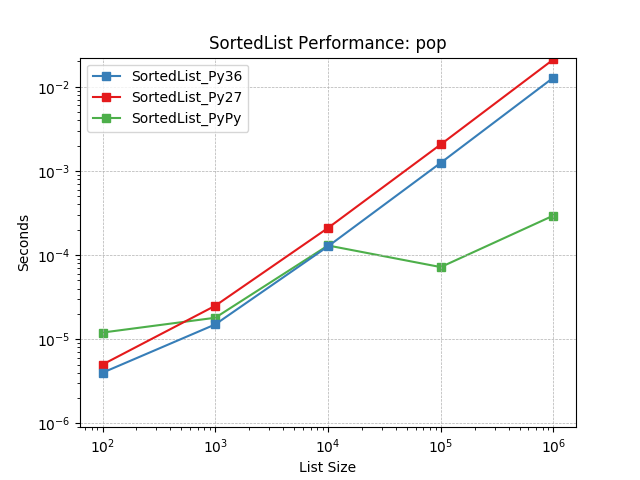
pop¶
Removing the last object using SortedList.pop().
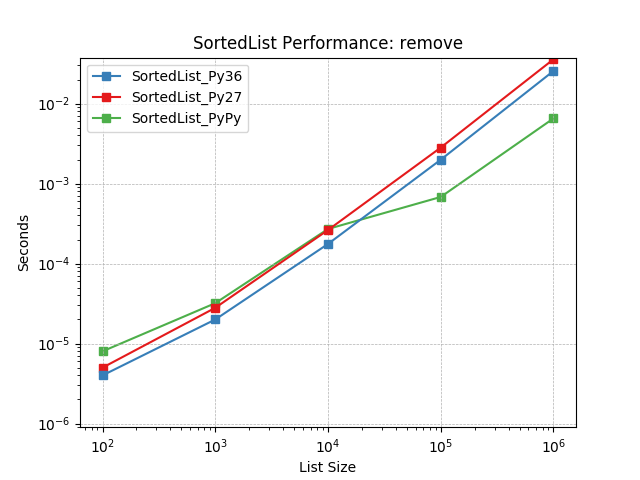
remove¶
Remove an object at random using SortedList.remove().
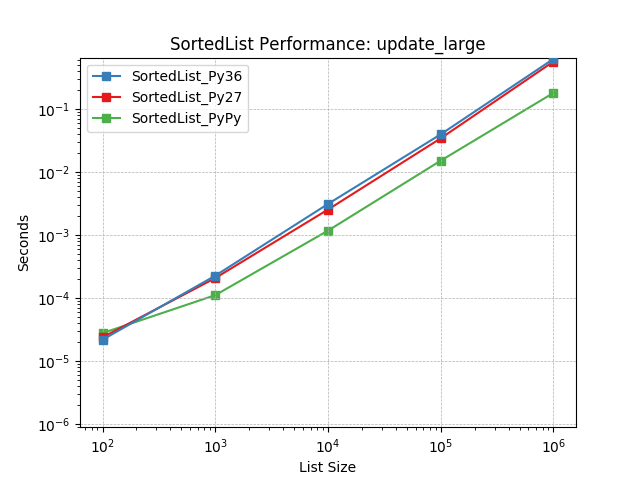
update_large¶
Updating a SortedList with a large iterable using SortedList.update().
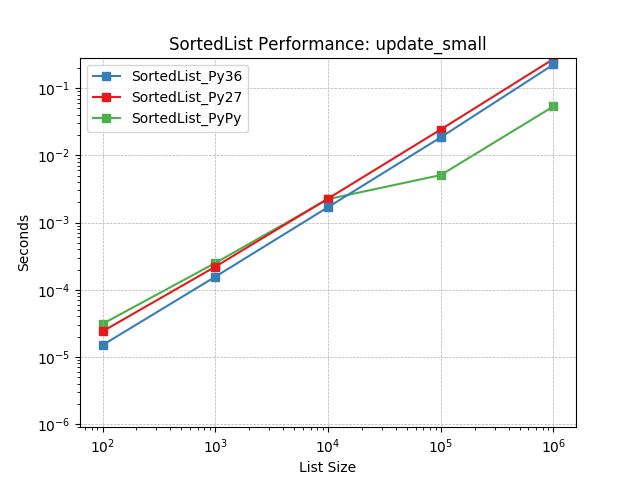
update_small¶
Updating a SortedList with a small iterable using SortedList.update().
Sorted Dict¶
Graphs comparing Sorted Dict performance.
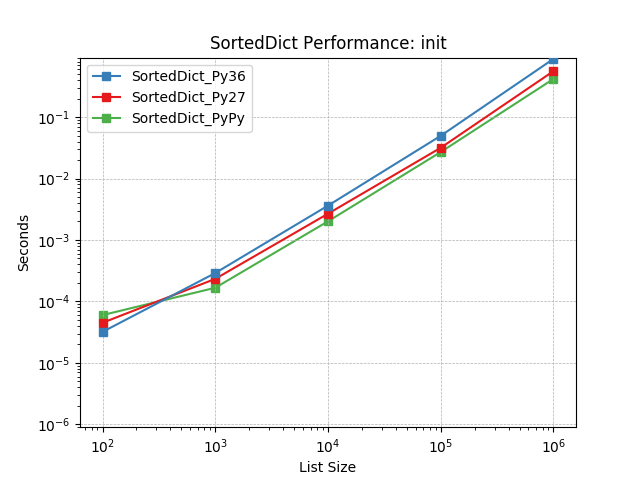
__init__¶
Initializing with a list of pairs of random numbers using
SortedDict.__init__().
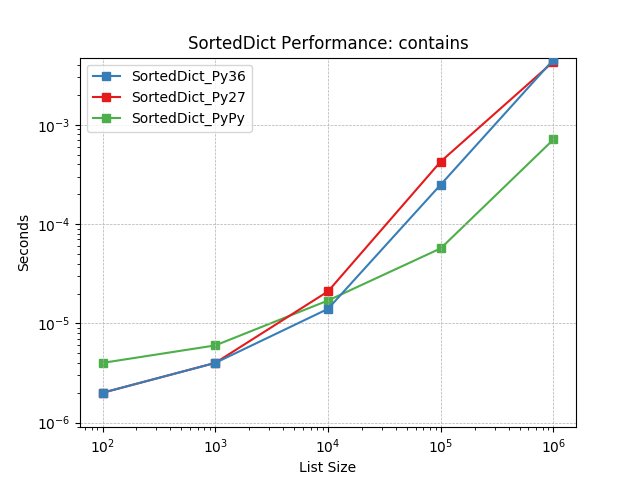
__contains__¶
Given a key at random, test whether the key is in the dictionary using
SortedDict.__contains__().
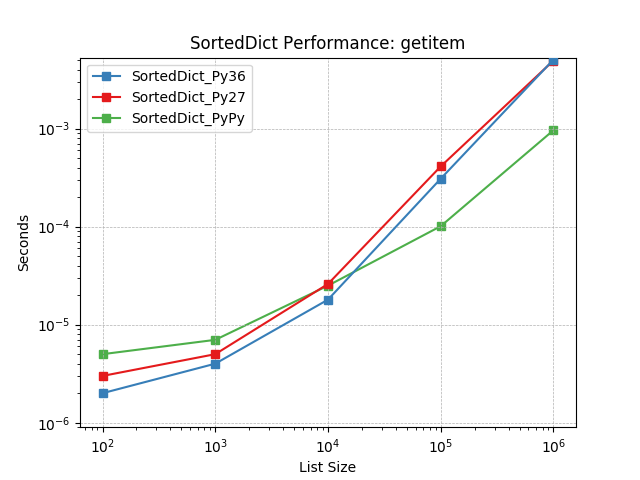
__getitem__¶
Given a key at random, retrieve the value using SortedDict.__getitem__().
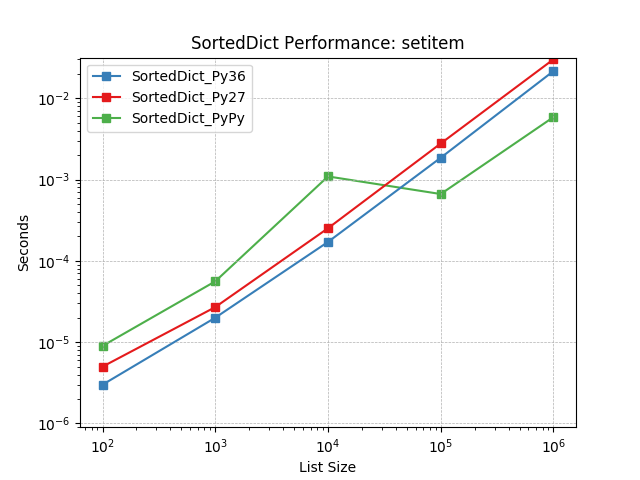
__setitem__¶
Given a key at random, set the value using SortedDict.__setitem__().
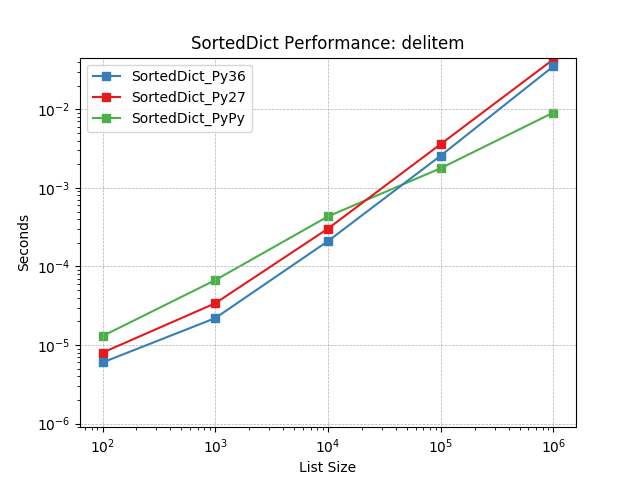
__delitem__¶
Given a key at random, delete the value using SortedDict.__delitem__().
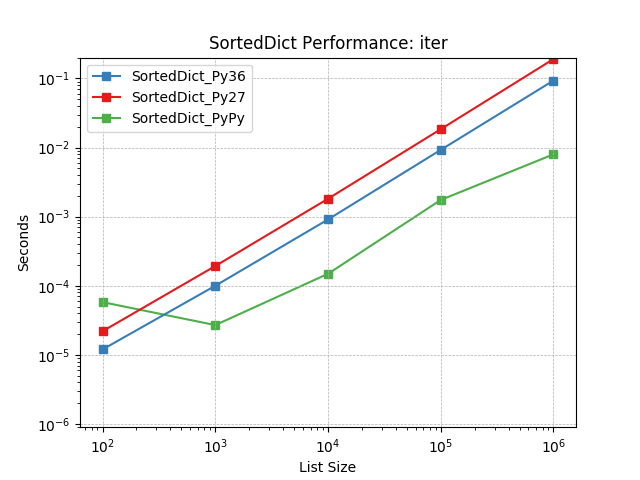
iter¶
Iterate the keys of a SortedDict using SortedDict.__iter__().
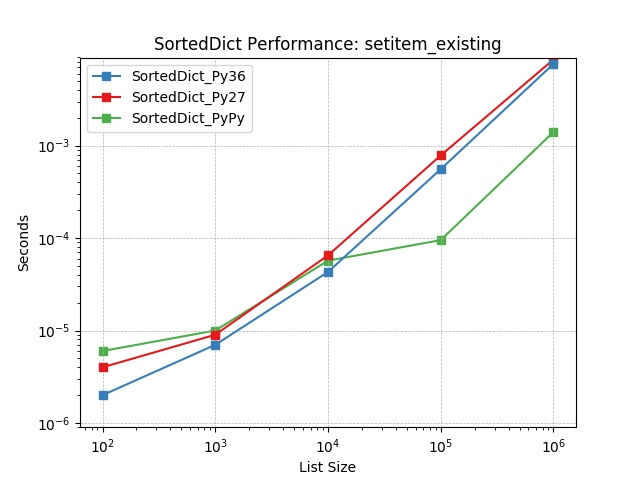
setitem_existing¶
Given an existing key at random, set the value using
SortedDict.__setitem__().
Sorted Set¶
Graphs comparing Sorted Set performance.
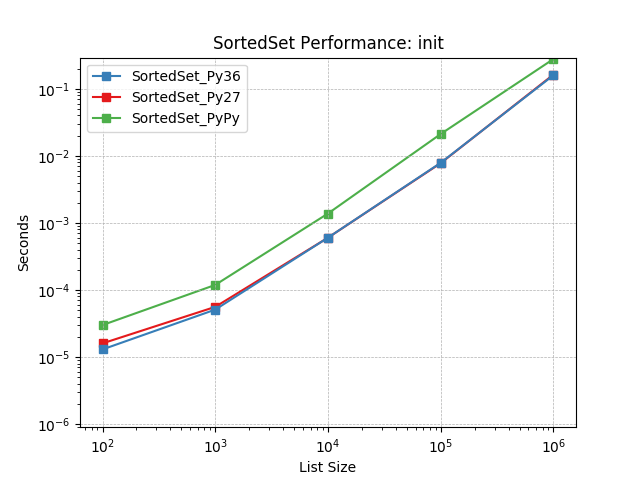
__init__¶
Initializing with a list of random numbers using SortedSet.__init__().
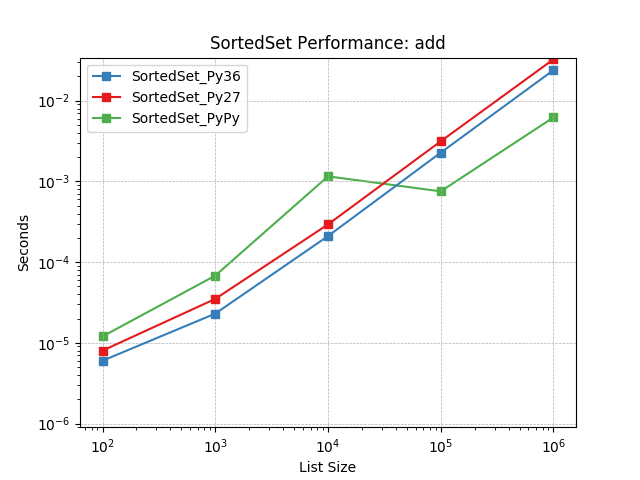
add¶
Randomly add values using SortedSet.add().
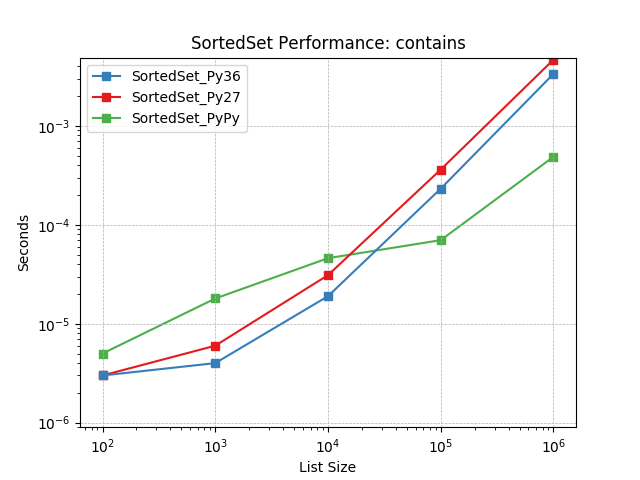
contains¶
Randomly test membership using SortedSet.__contains__().
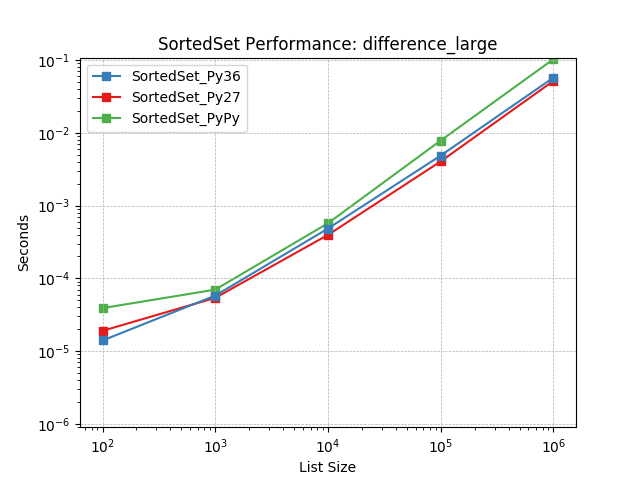
difference_large¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
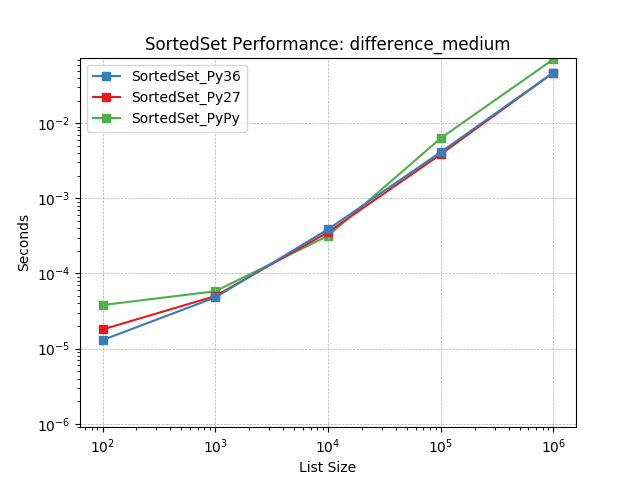
difference_medium¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
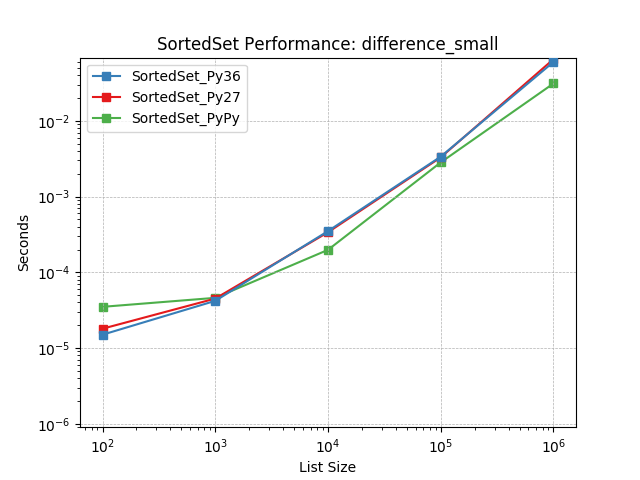
difference_small¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
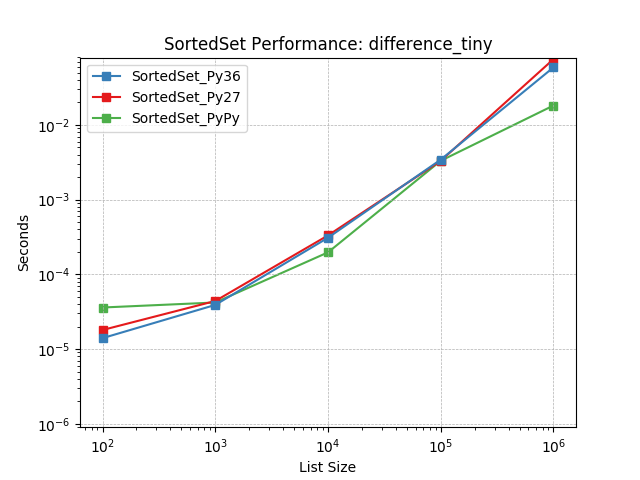
difference_tiny¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
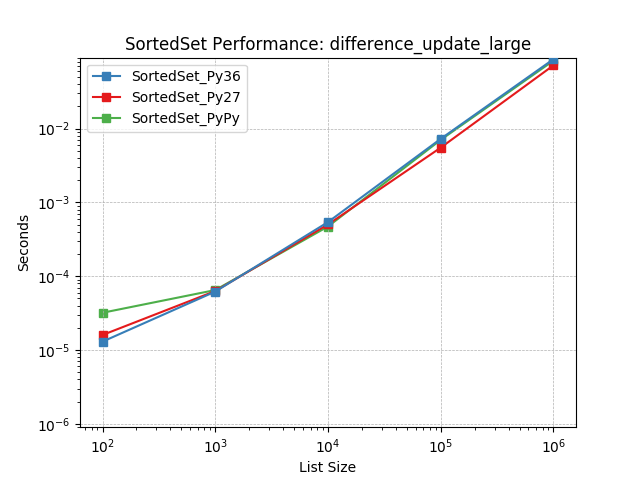
difference_update_large¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
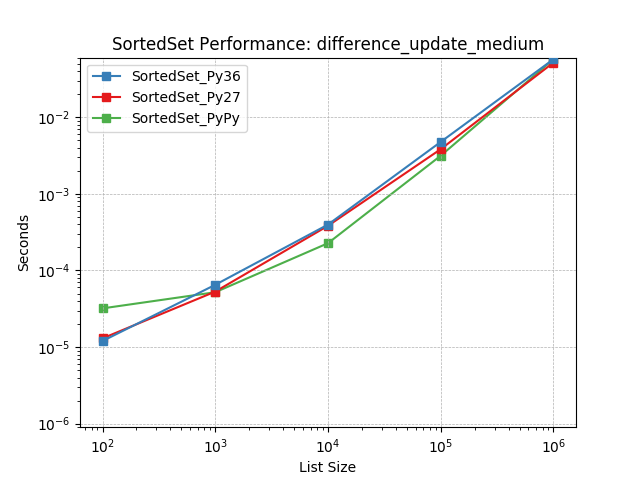
difference_update_medium¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
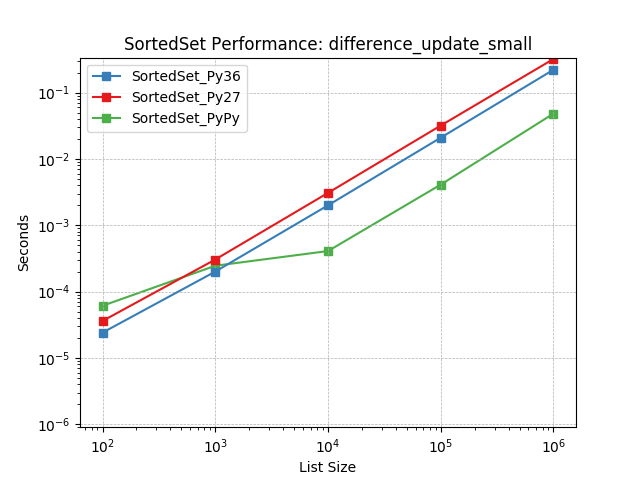
difference_update_small¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
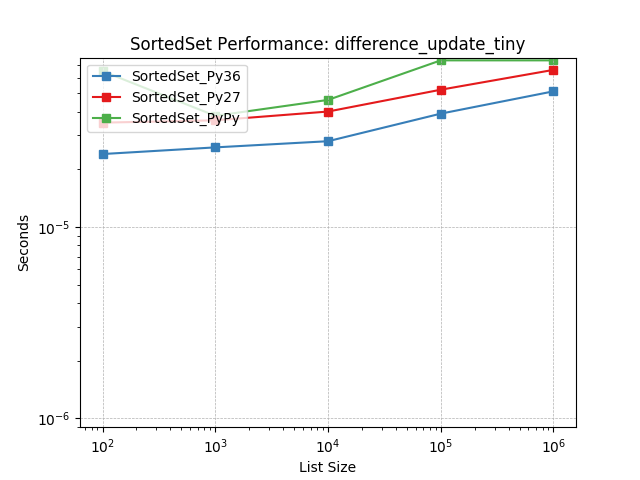
difference_update_tiny¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
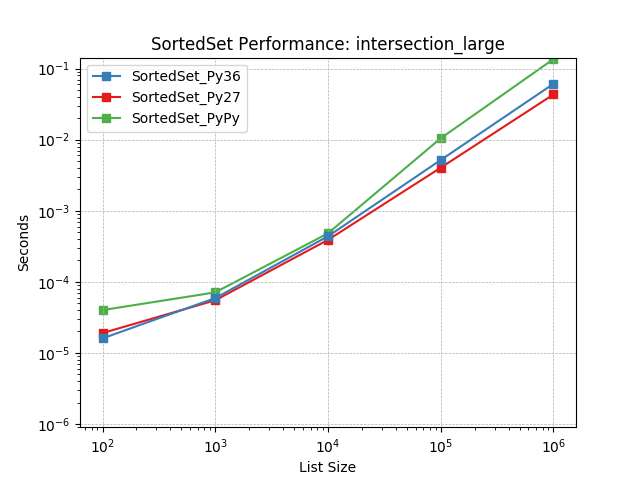
intersection_large¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
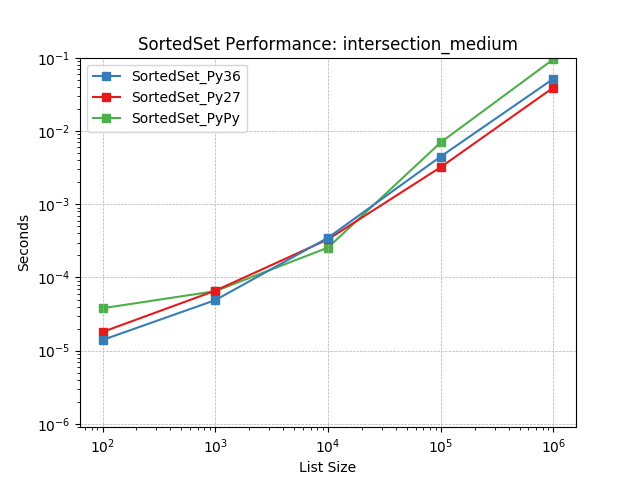
intersection_medium¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
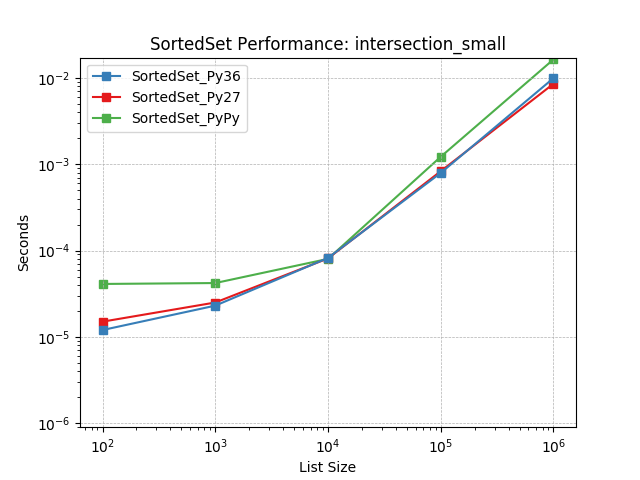
intersection_small¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
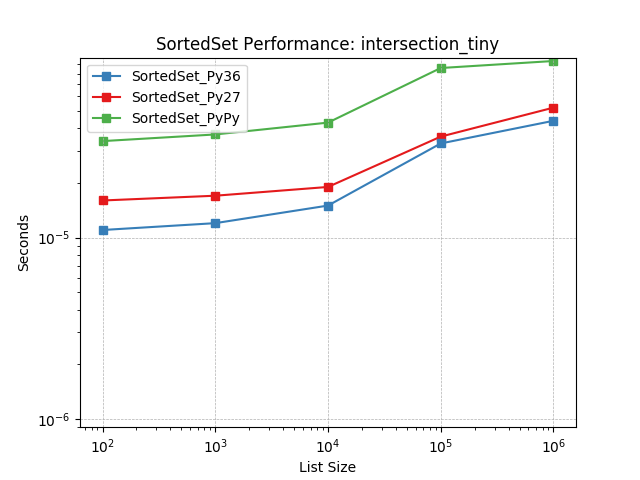
intersection_tiny¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
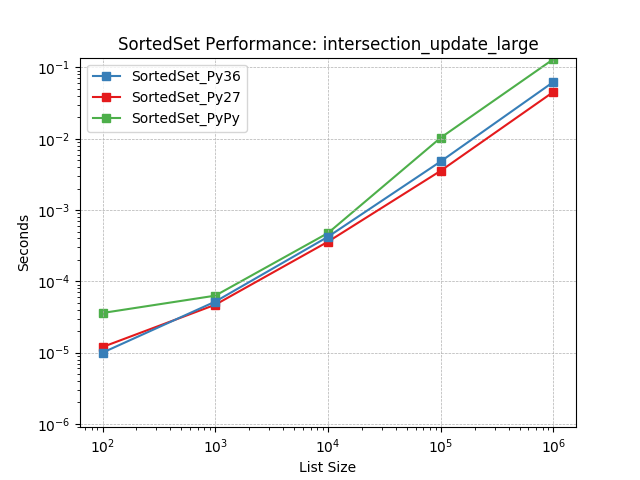
intersection_update_large¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
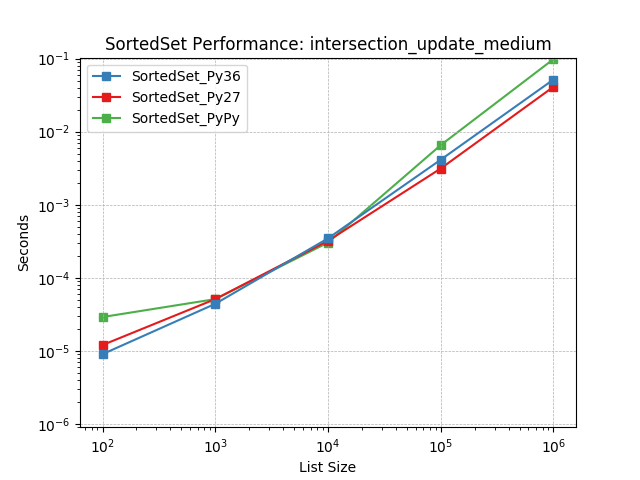
intersection_update_medium¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
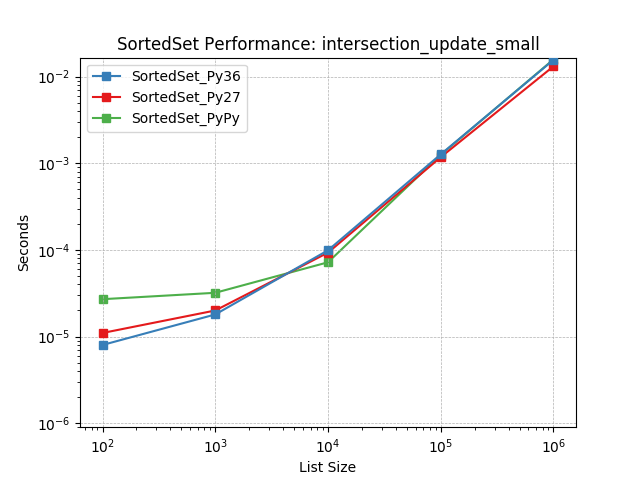
intersection_update_small¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
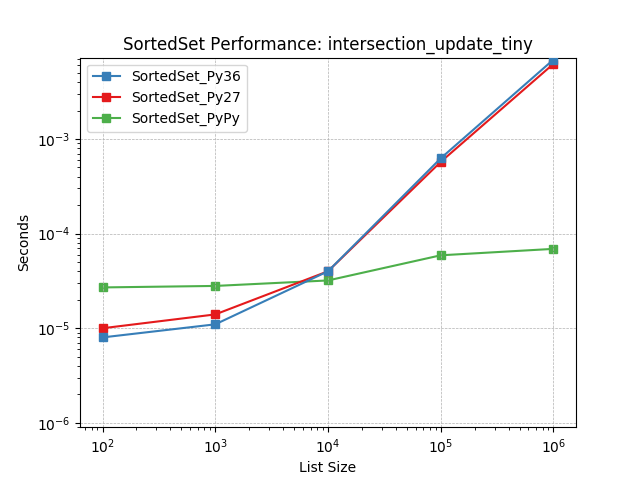
intersection_update_tiny¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
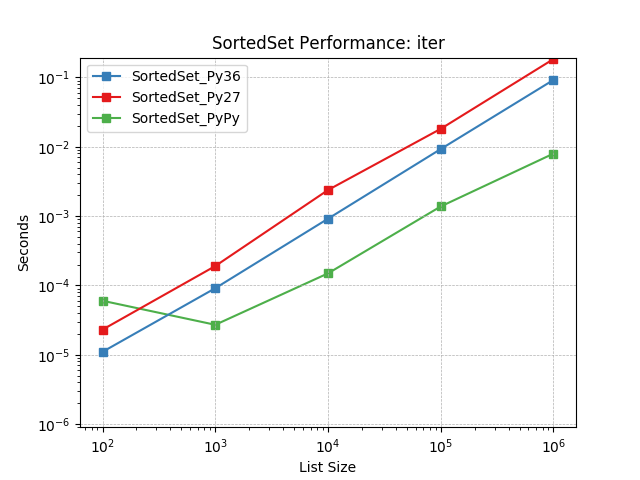
iter¶
Iterating a set using iter(SortedSet)().
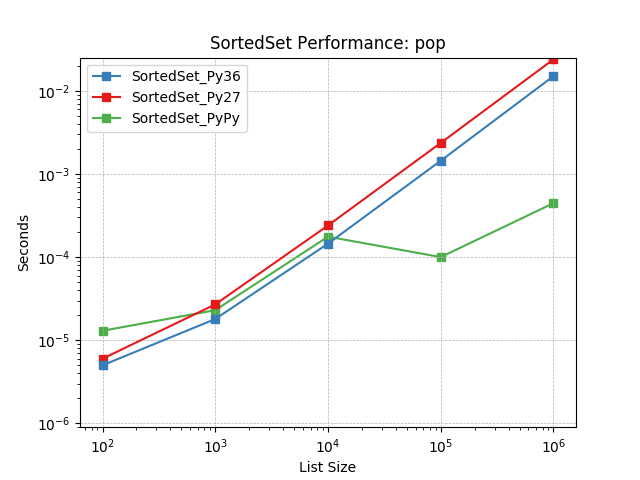
pop¶
Remove the last item in a set using SortedSet.pop().
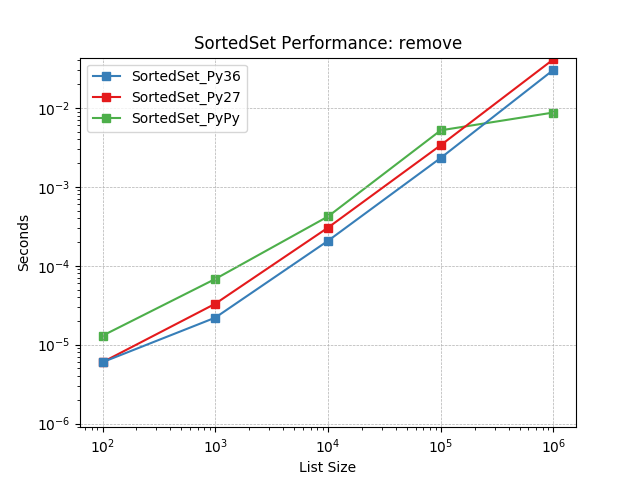
remove¶
Remove an item at random using SortedSet.remove().
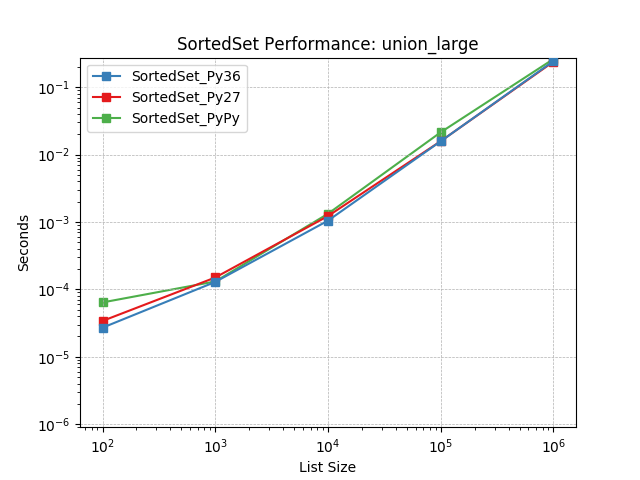
union_large¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
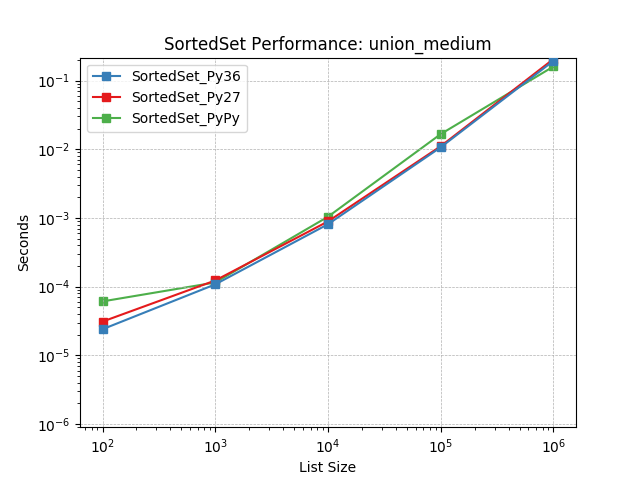
union_medium¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
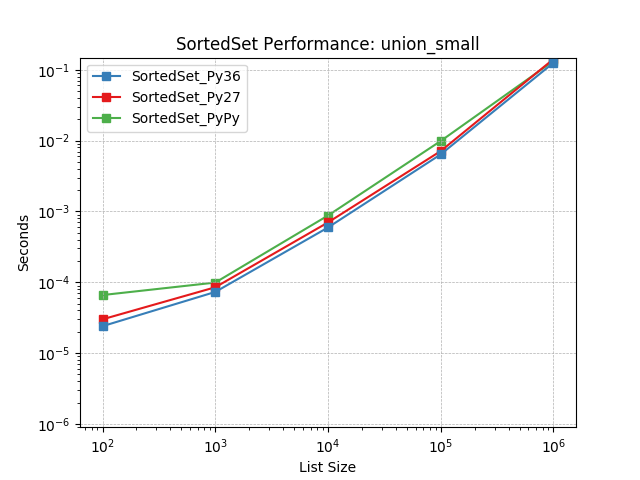
union_small¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
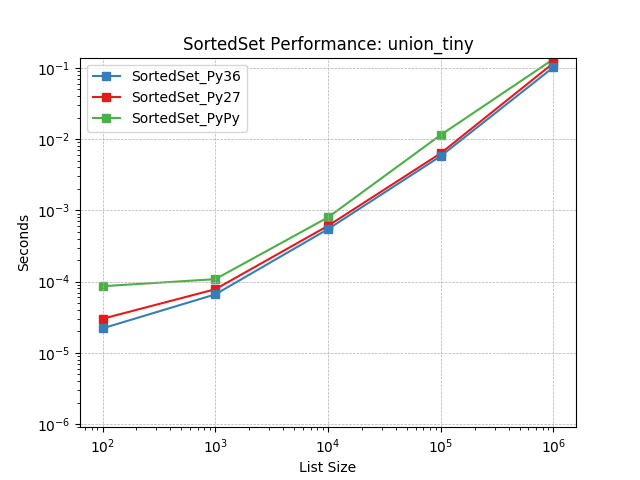
union_tiny¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
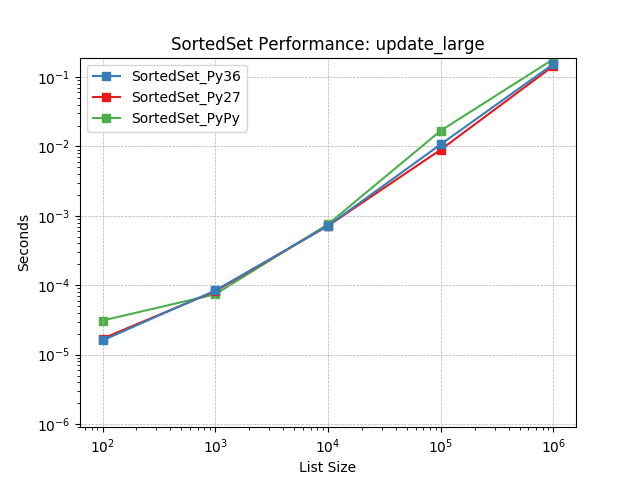
update_large¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
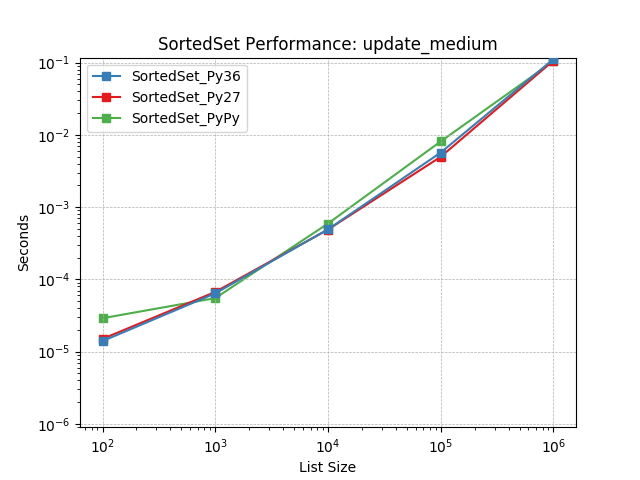
update_medium¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
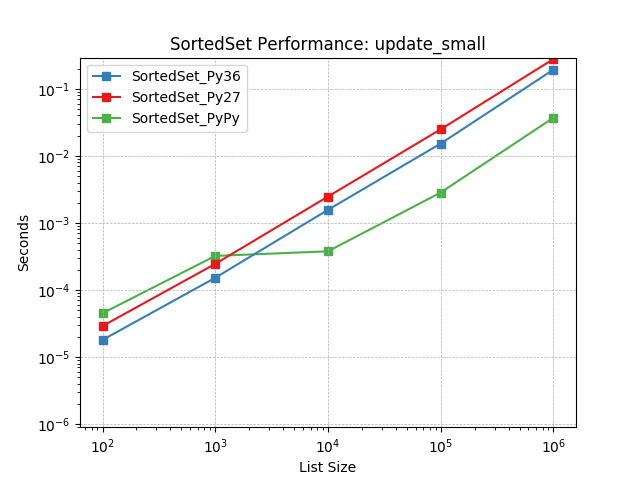
update_small¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
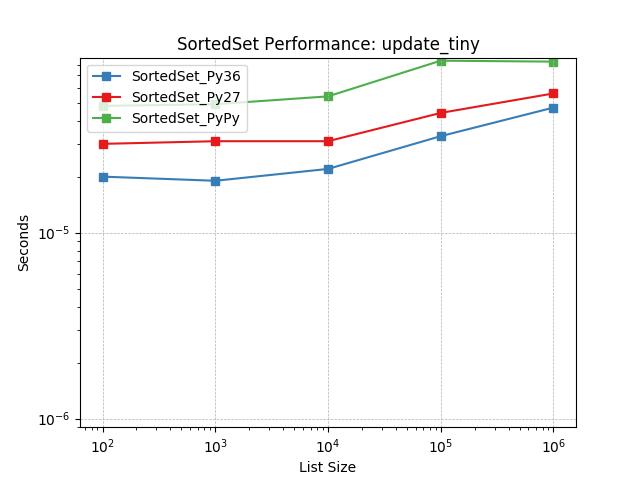
update_tiny¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
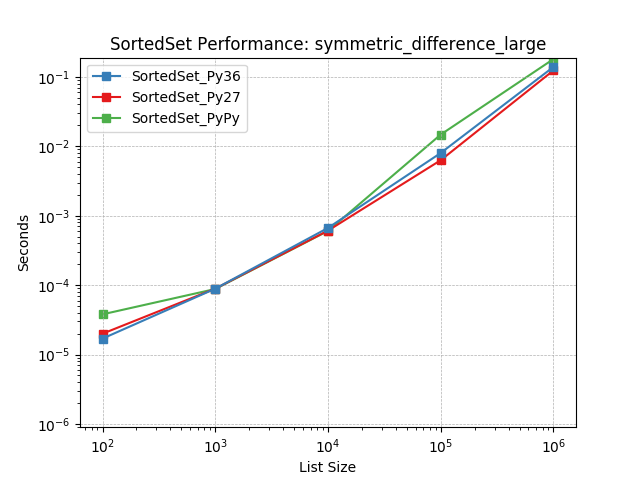
symmetric_difference_large¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
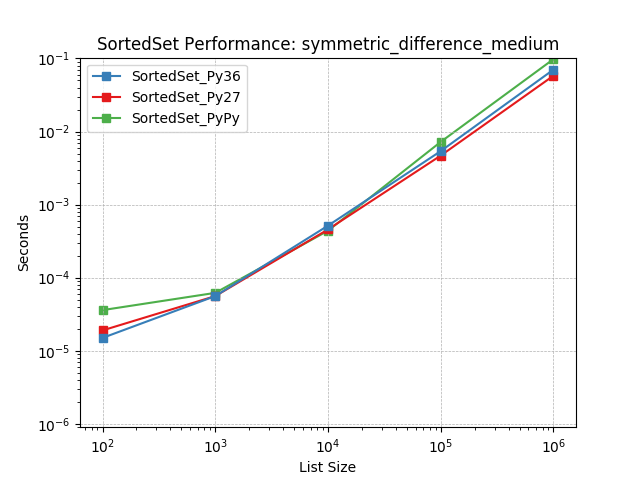
symmetric_difference_medium¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
symmetric_difference_small¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
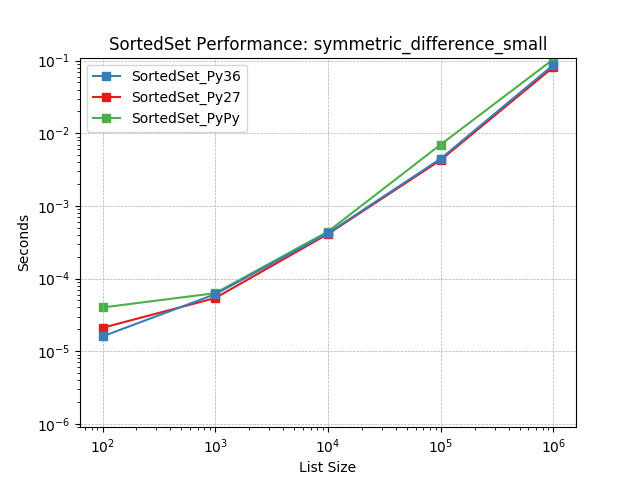
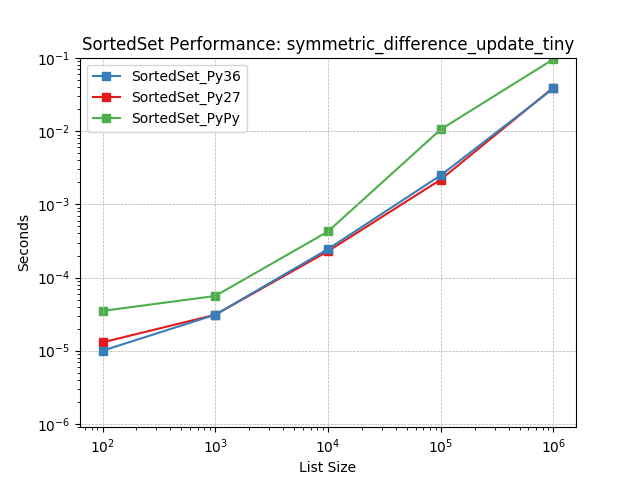
symmetric_difference_tiny¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
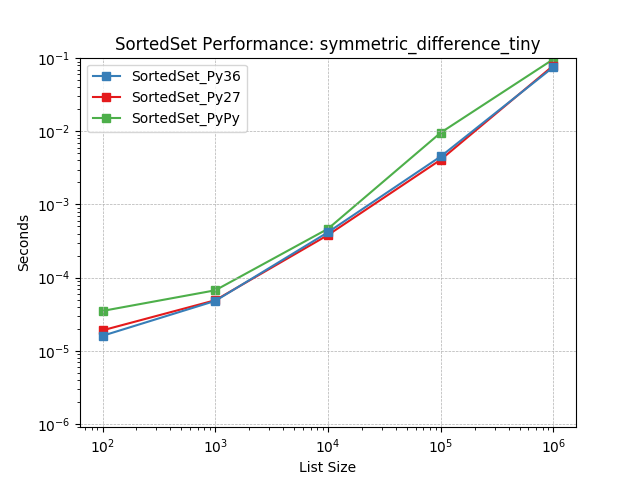
symm_diff_update_large¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().
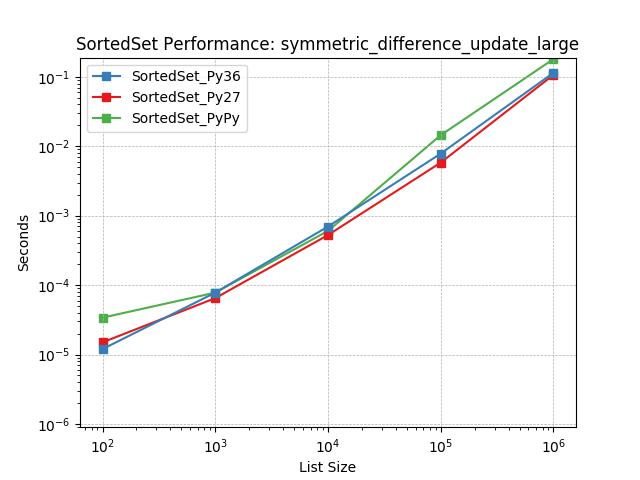
symm_diff_update_medium¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().
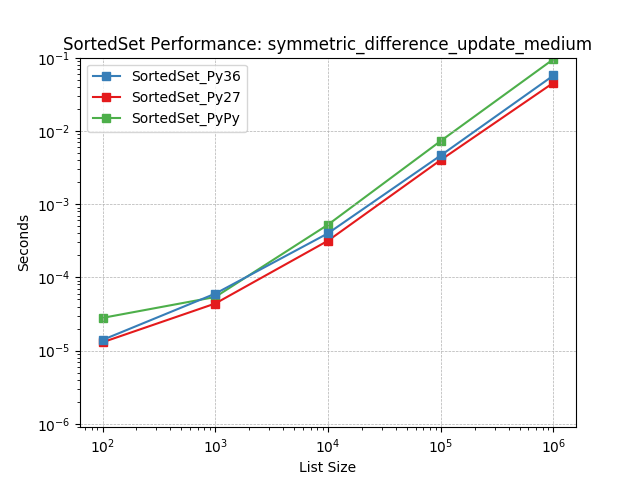
symm_diff_update_small¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().
symm_diff_update_tiny¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().