Performance Comparison¶
Measuring performance is a difficult task. All the benchmarks on this page are synthetic in the sense that they test one function repeatedly. Measurements in live systems are much harder to produce reliably. So take the following data with a grain of salt. That being said, a stated feature of Sorted Containers is performance so we would be remiss not to produce this page with comparisons.
The source for all benchmarks can be found under the “tests” directory in the files prefixed “benchmark.” Measurements are made from the min, max, and median of 5 repetitions. In the graphs below, the line follows the median at each point. Note that the axes are log-log so properly reading two different lines would describe one metric as “X times” faster rather than “X seconds” faster. In all graphs, lower is better. Measurements are made by powers of ten: 100 through 10,000,000.
Measurements up to ten billion elements have been successfully tested and benchmarked. Read Performance at Scale for details. Only a couple implementations (including Sorted Containers) are capable of handling so many elements. The major limiting factor at that size is memory. Consider the simple case of storing CPython’s integers in a Sorted List. Each integer object requires ~24 bytes so one hundred million elements will require about three gigabytes of memory. If the implementation adds significant overhead then most systems will run out of memory. For all datasets which may be kept in memory, Sorted Containers is an excellent choice.
A good effort has been made to find competing implementations. Seven in total were found with various list, set, and dict implementations.
blist – Provides list, dict, and set containers based on the blist data-type. Uses a B-Tree data structure. Implemented in Python and C. BSD License. Last updated March, 2014. blist on PyPI
bintrees – Provides several tree-based implementations for dict and set containers. Fastest were AVL-Tree and Red-Black-Tree data structures.. Extends the conventional API to provide set operations for the dict type. Now deprecated in favor of Sorted Containers Implemented in C. MIT License. Last updated April, 2017. bintrees on PyPI
sortedmap – Provides a fast, C++ implementation for dict data types. Uses the C++ standard library std::map data structure which is usually a red-black tree. Last updated February, 2016. sortedmap on PyPI
banyan – Provides a fast, C++ implementation for dict and set data types. Offers some features also found in sortedcontainers like accessing the n-th item in a set or dict. Uses sources from the tree implementation in GNU libstdc++. GPLv3 License. Last updated April, 2013. banyan on PyPI
treap – Uses Cython for improved performance and provides a dict container. Apache V2 License. Last updated June, 2017. treap on PyPI
skiplistcollections – Pure-Python implementation based on skip-lists providing a limited API for dict and set types. MIT License. Last updated January, 2014. skiplistcollections on PyPI
sortedcollection – Pure-Python implementation of sorted list based solely on a list. Feature-poor and inefficient for writes but included because it is written by Raymond Hettinger and linked from the official Python docs. MIT License. Last updated April, 2011. sortedcollection recipe
Several alternative implementations were omitted for reasons documented below:
rbtree – C-implementation that only supports Python 2. Provides a fast, C-implementation for dict and set data types. GPLv3 License. Last updated March, 2012. rbtree on PyPI
ruamel.ordereddict.sorteddict – C-implementation that only supports Python 2. Performance was measured in correspondence with the module author. Performance was generally very good except for
__delitem__. At scale, deleting entries became exceedingly slow. MIT License. Last updated July, 2017. ruamel.ordereddict on PyPIpyskiplist – Pure-Python skip-list based implementation supporting a sorted-list-like interface. Now deprecated in favor of Sorted Containers. MIT License. Last updated July, 2015. pyskiplist on PyPI
sorteddict – Pure-Python lazily-computed sorted dict implementation. Now deprecated in favor of Sorted Containers. GPLv3 License. Last updated September, 2007. sorteddict on PyPI
rbtree from NewCenturyComputers – Pure-Python tree-based implementation. Not sure when this was last updated. Unlikely to be fast. Unknown license. Unknown last update. rbtree from NewCenturyComputers
python-avl-tree from GitHub user pgrafov – Pure-Python tree-based implementation. Unlikely to be fast. MIT License. Last updated October, 2010. python-avl-tree from GitHub user pgrafov
pyavl – C-implementation for AVL tree-based dict and set containers. Claims to be fast. Lacking documentation and failed to build. Public Domain License. Last updated December, 2008. pyavl on PyPI
skiplist – C-implementation of sorted list based on skip-list data structure. Only supports Python 2. Zlib/libpng License. Last updated Septemeber, 2013. skiplist from Bitbucket user mojaves
The most similar module to Sorted Containers is skiplistcollections given that each is implemented in Python. But as is displayed below, Sorted Containers is several times faster and provides a richer API. Often the pure-Python implementation in Sorted Containers is faster even than the C-implementation counterparts. Where it lacks, performance is generally on the same magnitude.
Because Sorted Containers is implemented in pure-Python, its performance depends directly on the Python runtime. A runtime performance comparison is also included with data from popular runtimes.
Sorted Containers uses a segmented-list data structure similar to a B-tree limited to two levels of nodes. As part of the implementation, a load factor is used to determine how many values should be stored in each node. This can have a significant impact on performance and a load factor performance comparison is also provided.
Though these benchmarks exercise only one API repeatedly, an effort has also been made to simulate real-world workloads. The simulated workload performance comparison contains examples with comparisons to other implementations, load factors, and runtimes.
Some final notes about the graphs below. Missing data indicates the benchmark either took too long or failed. The set operations with tiny, small, medium, and large variations indicate the size of the container involved in the right-hand-side of the operation: tiny is exactly 10 elements; small is 10% of the size of the left-hand-side; medium is 50%; and large is 100%. Sorted Containers uses a different algorithm based on the size of the right-hand-side of the operation for a dramatic improvement in performance.
The legends of the graphs below correlate the underlying data structure used the Python project. The correlation is as follows:
Data Structure |
Project |
|---|---|
B-Tree |
|
List |
|
AVL-Tree |
|
RB-Tree |
|
Skip-List |
|
std::map |
|
Treap |
Sorted List¶
Graphs comparing Sorted List performance.
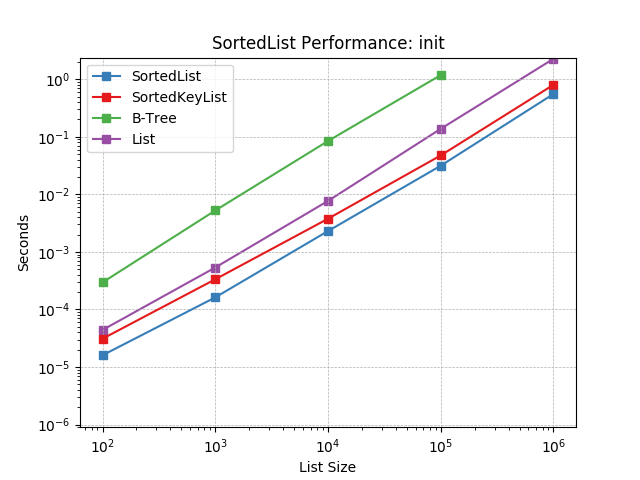
__init__¶
Initializing with a list of random numbers using SortedList.__init__().
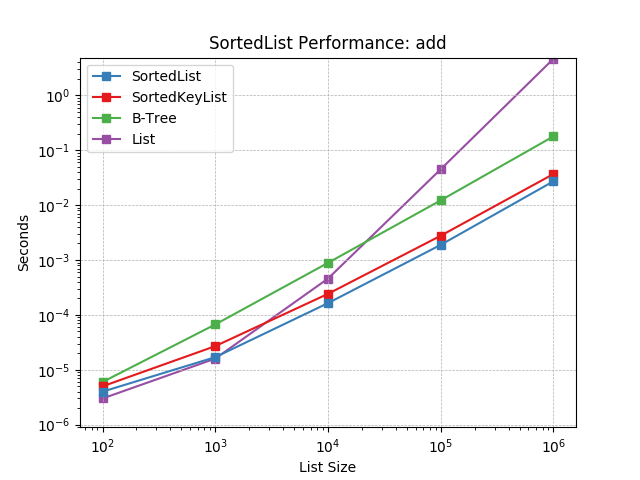
add¶
Randomly adding values using SortedList.add().
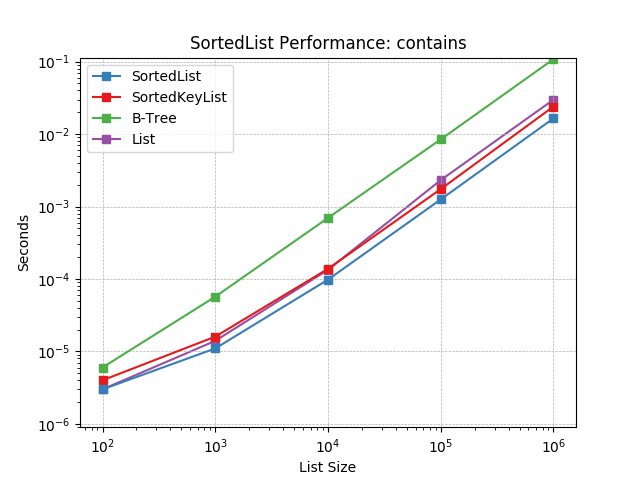
contains¶
Randomly testing membership using SortedList.__contains__().
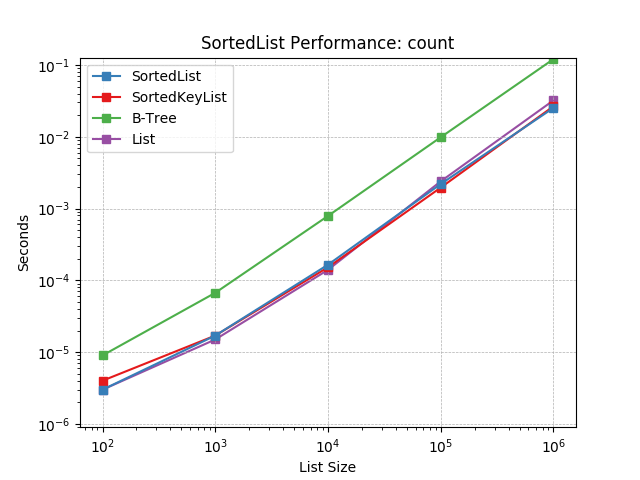
count¶
Counting objects at random using SortedList.count().
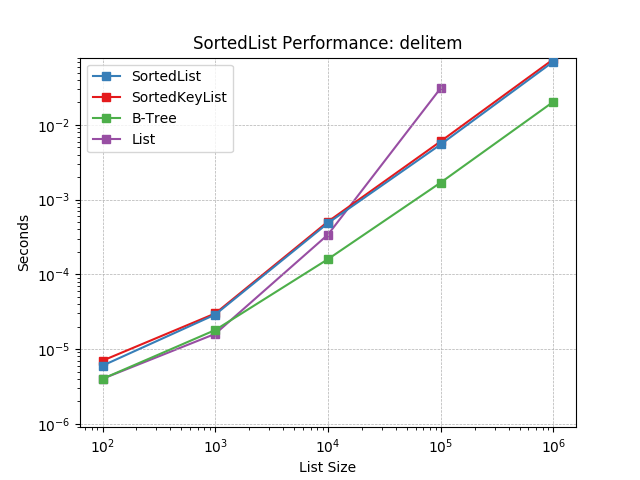
__delitem__¶
Deleting objects at random using SortedList.__delitem__().
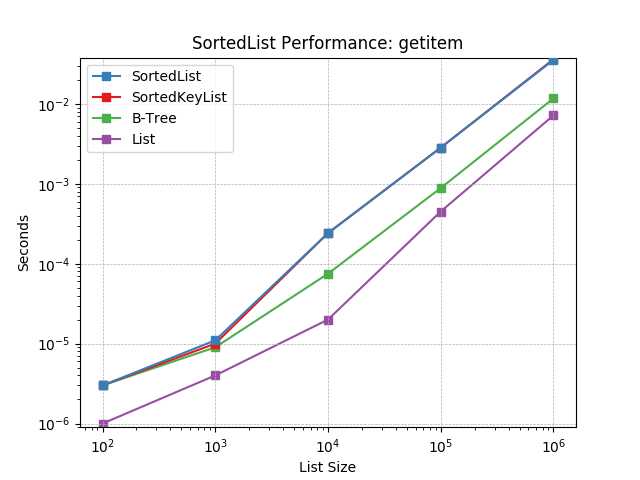
__getitem__¶
Retrieving objects by index using SortedList.__getitem__().
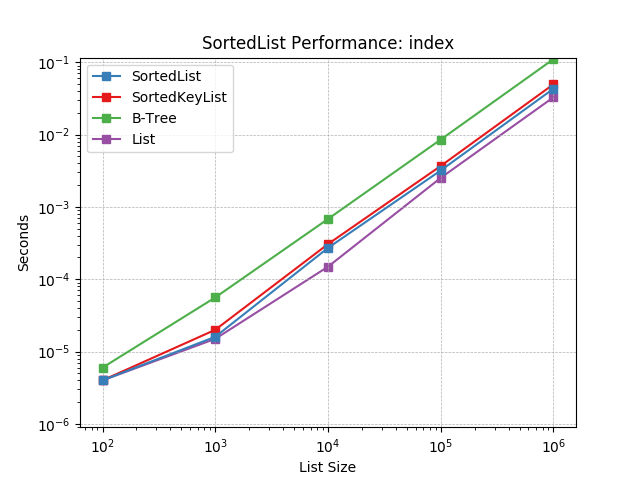
index¶
Finding the index of an object using SortedList.index().
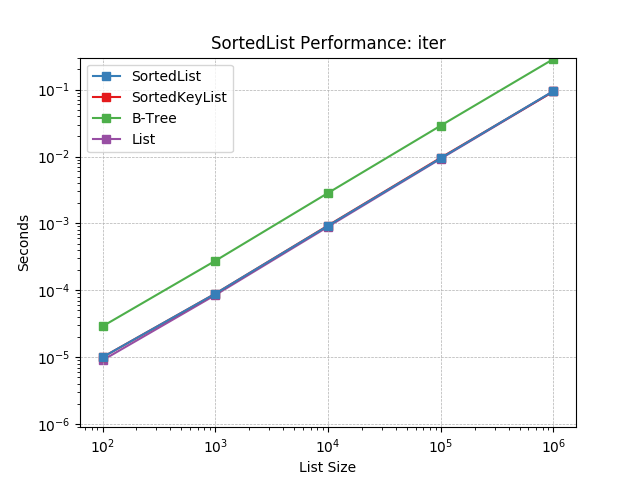
iter¶
Iterating a SortedList using SortedList.__iter__().
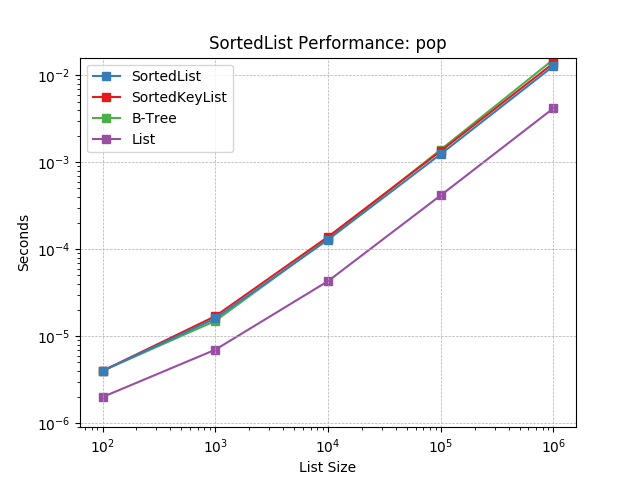
pop¶
Removing the last object using SortedList.pop().
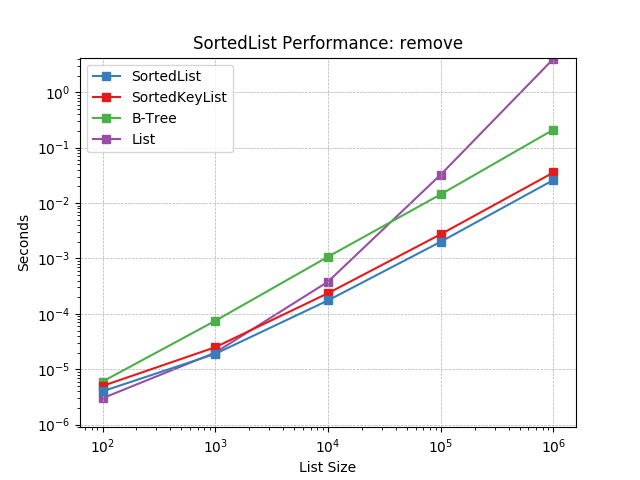
remove¶
Remove an object at random using SortedList.remove().
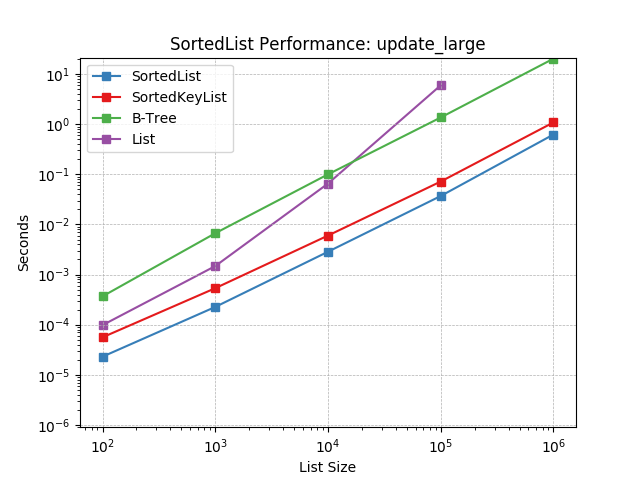
update_large¶
Updating a SortedList with a large iterable using SortedList.update().
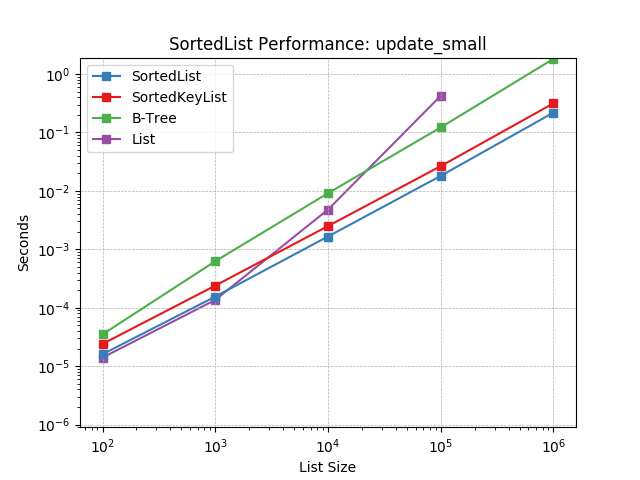
update_small¶
Updating a SortedList with a small iterable using SortedList.update().
Sorted Dict¶
Graphs comparing Sorted Dict performance.
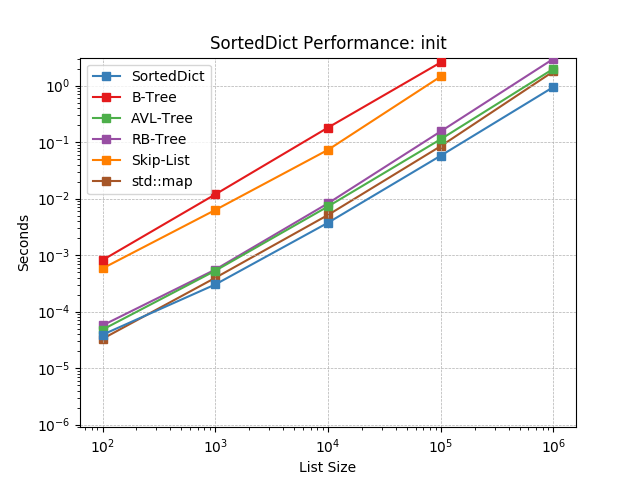
__init__¶
Initializing with a list of pairs of random numbers using
SortedDict.__init__().
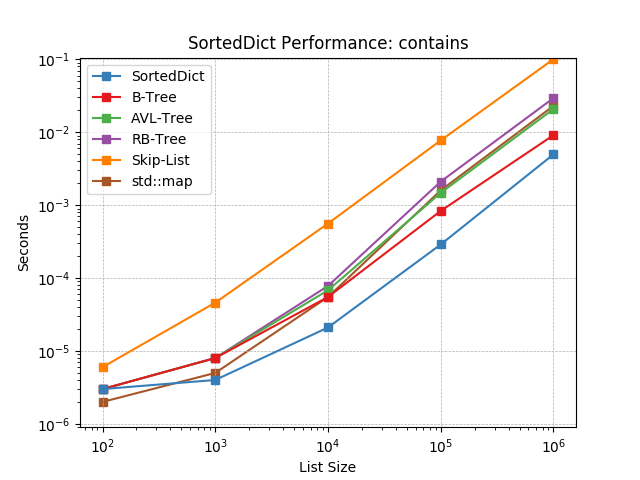
__contains__¶
Given a key at random, test whether the key is in the dictionary using
SortedDict.__contains__().
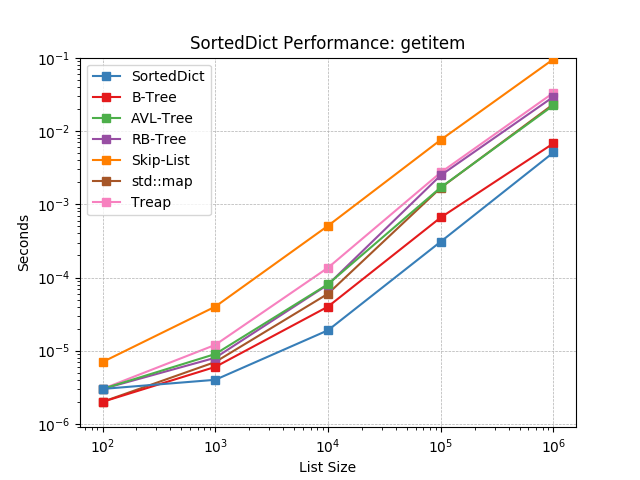
__getitem__¶
Given a key at random, retrieve the value using SortedDict.__getitem__().
__setitem__¶
Given a key at random, set the value using SortedDict.__setitem__().
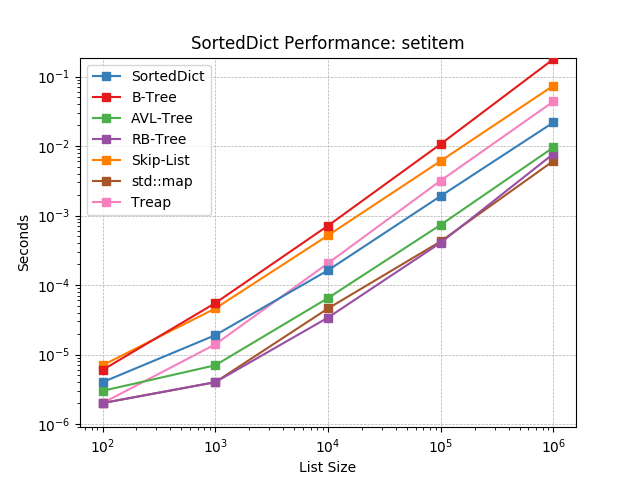
__delitem__¶
Given a key at random, delete the value using SortedDict.__delitem__().
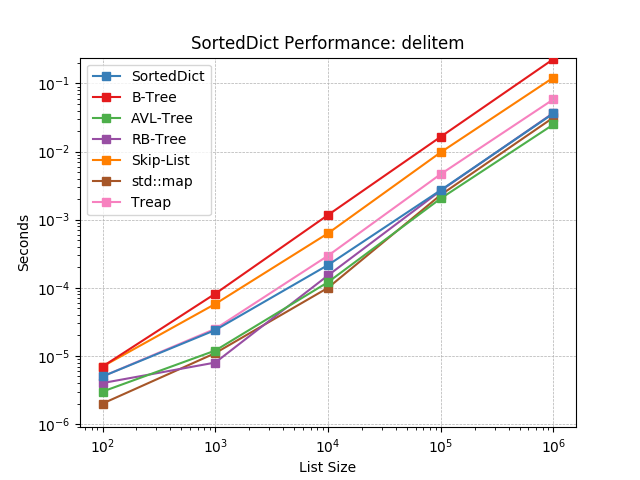
iter¶
Iterate the keys of a SortedDict using SortedDict.__iter__().
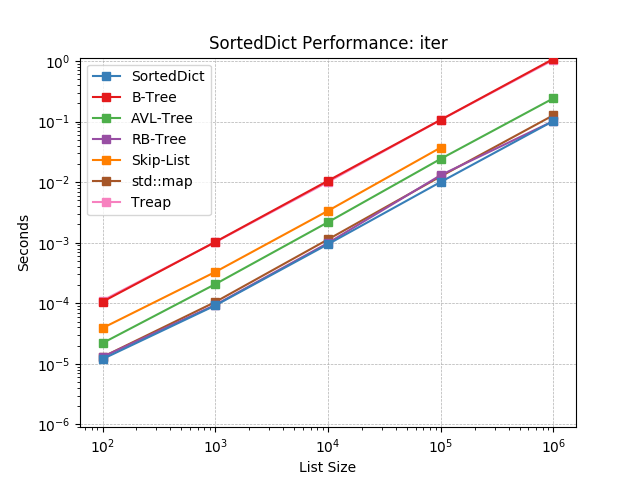
setitem_existing¶
Given an existing key at random, set the value using
SortedDict.__setitem__().
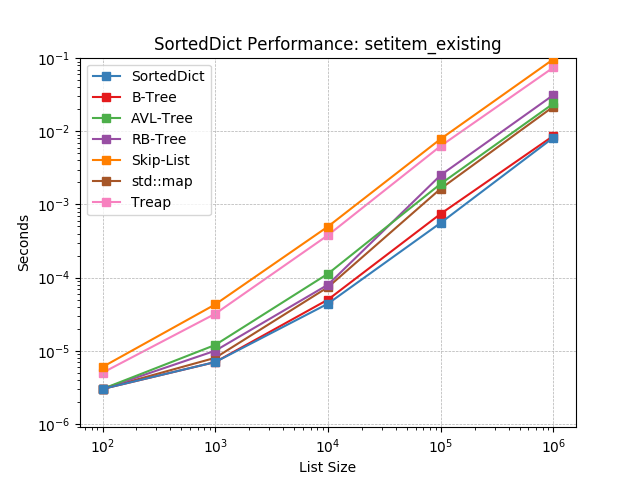
Sorted Set¶
Graphs comparing Sorted Set performance.
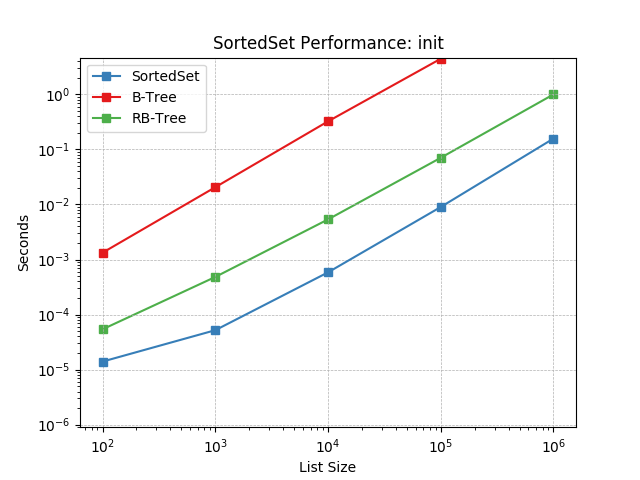
__init__¶
Initializing with a list of random numbers using SortedSet.__init__().
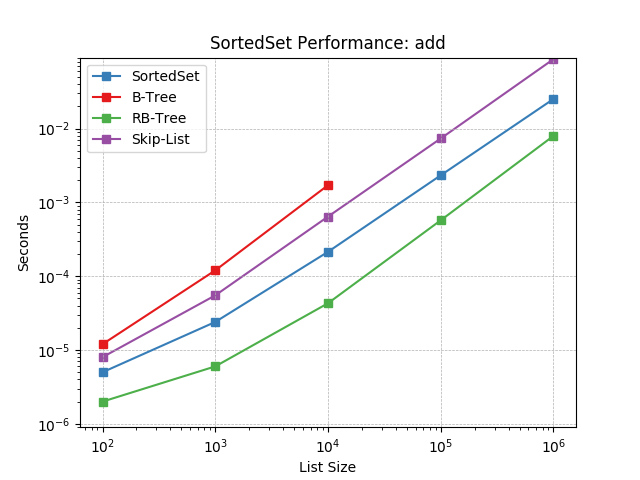
add¶
Randomly add values using SortedSet.add().
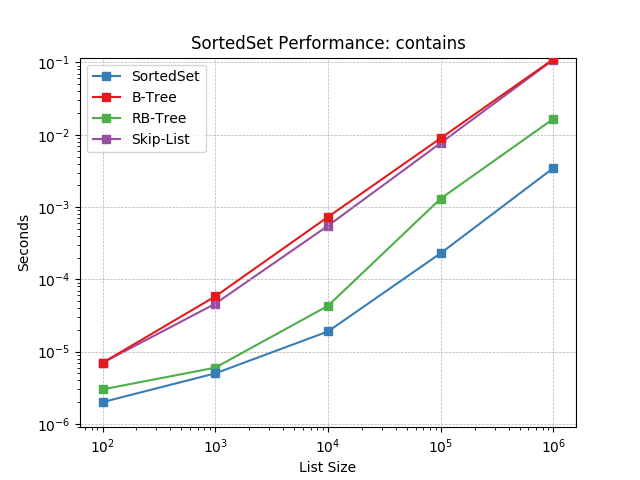
contains¶
Randomly test membership using SortedSet.__contains__().
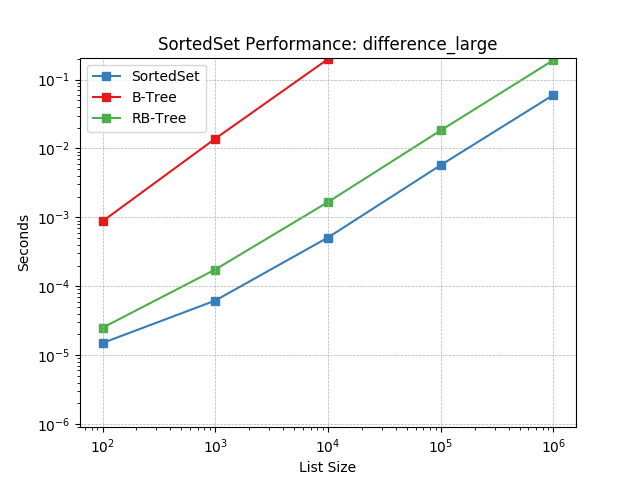
difference_large¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
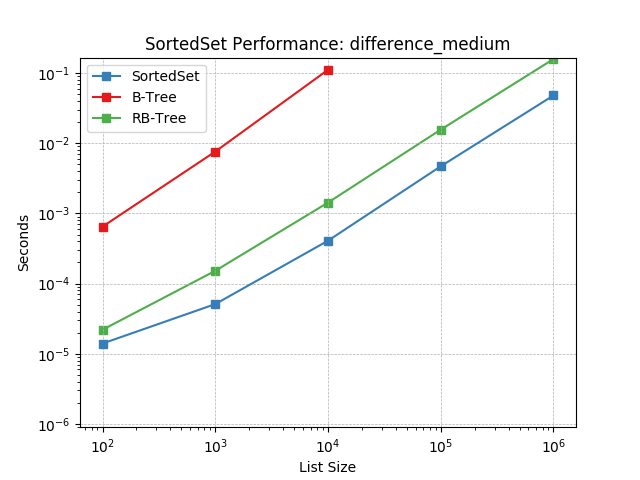
difference_medium¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
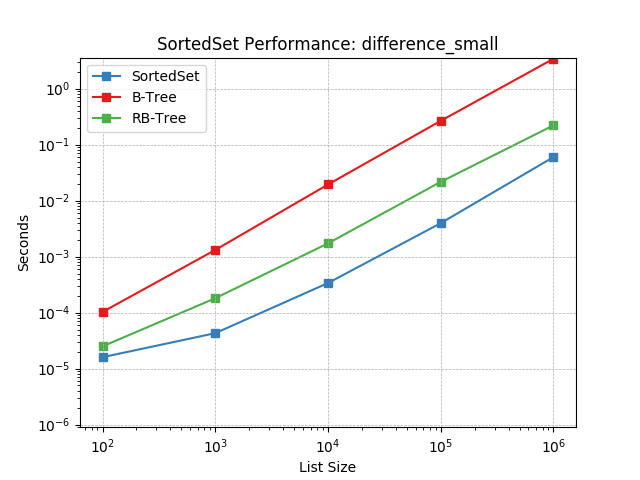
difference_small¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
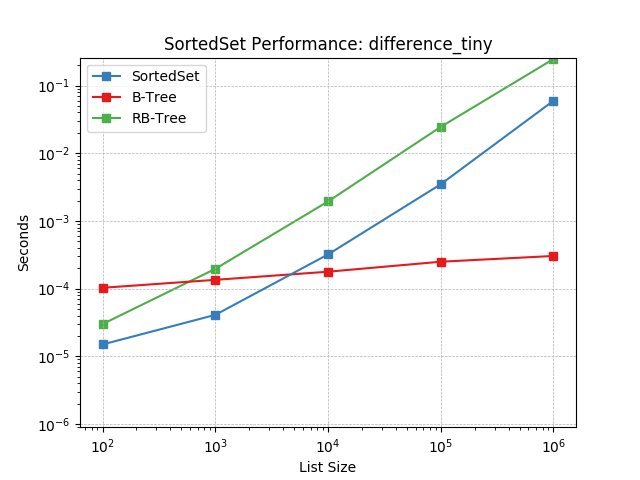
difference_tiny¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference().
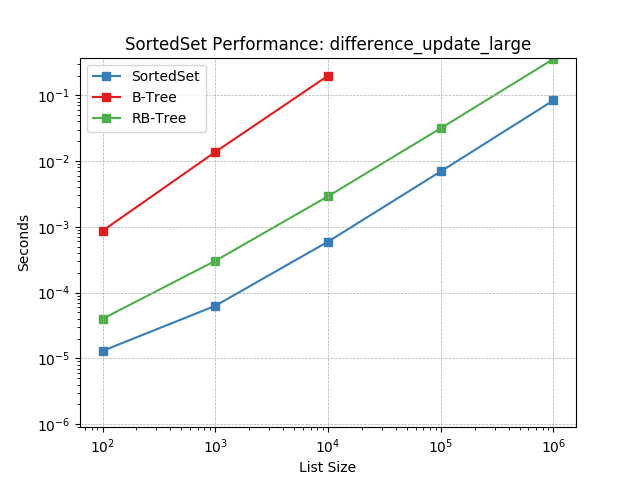
difference_update_large¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
difference_update_medium¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
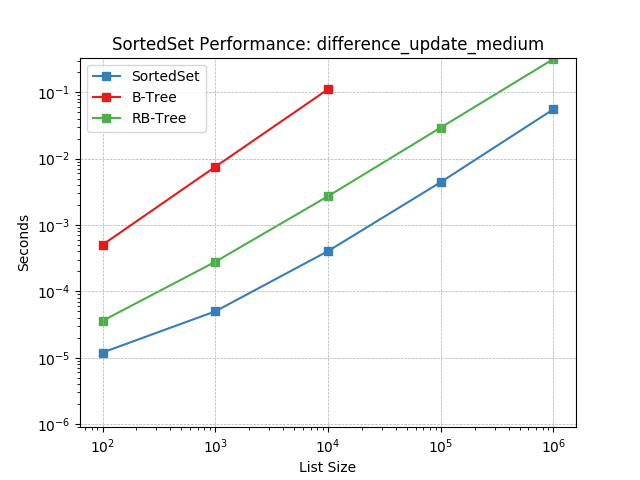
difference_update_small¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
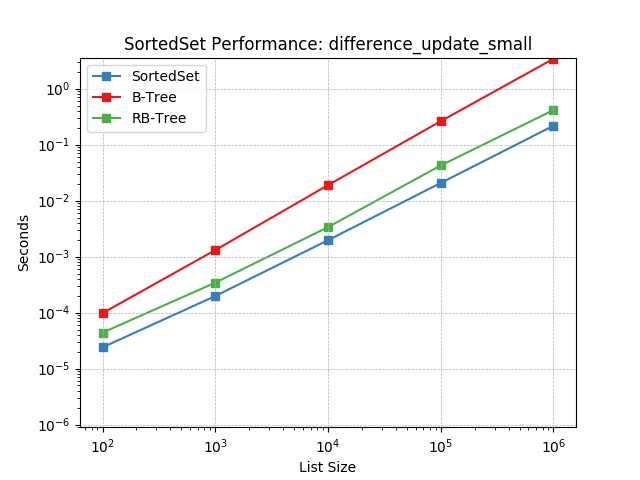
difference_update_tiny¶
Set difference using SortedSet.difference_update().
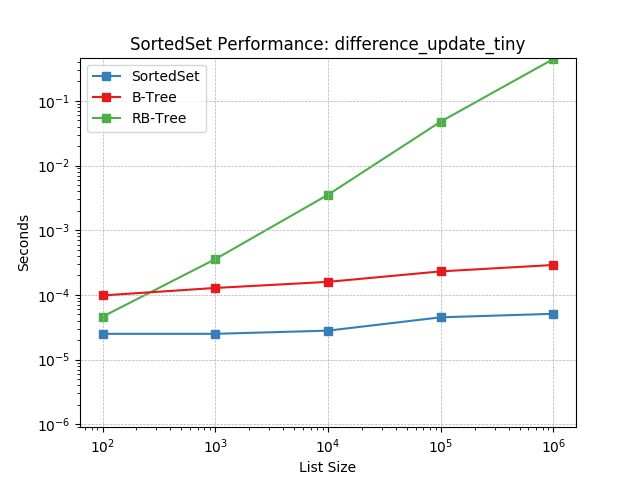
intersection_large¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
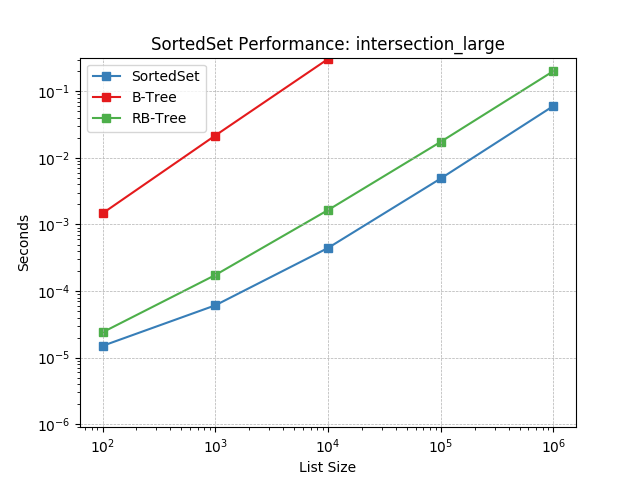
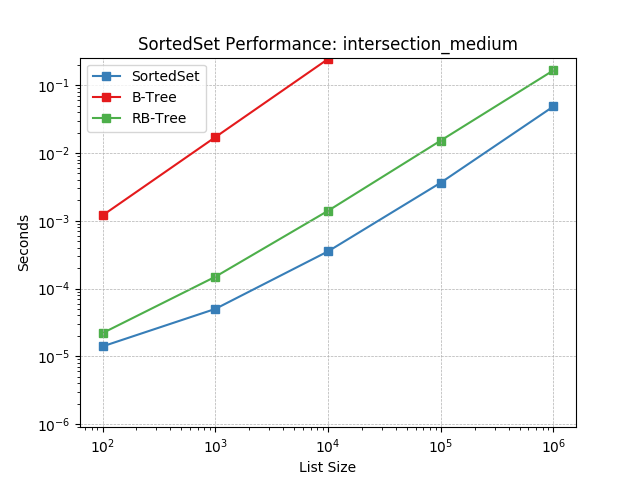
intersection_medium¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
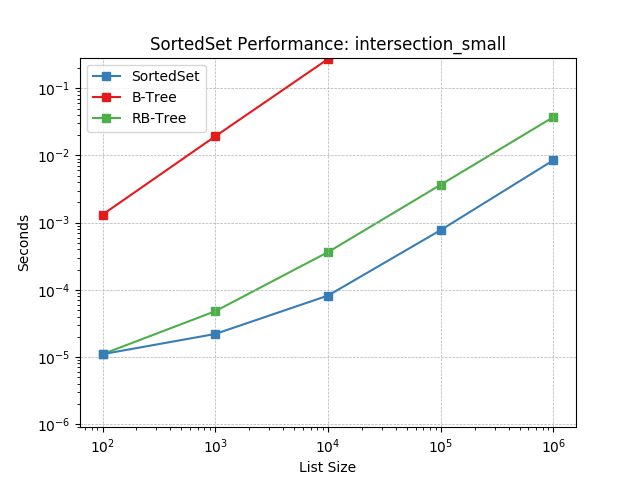
intersection_small¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
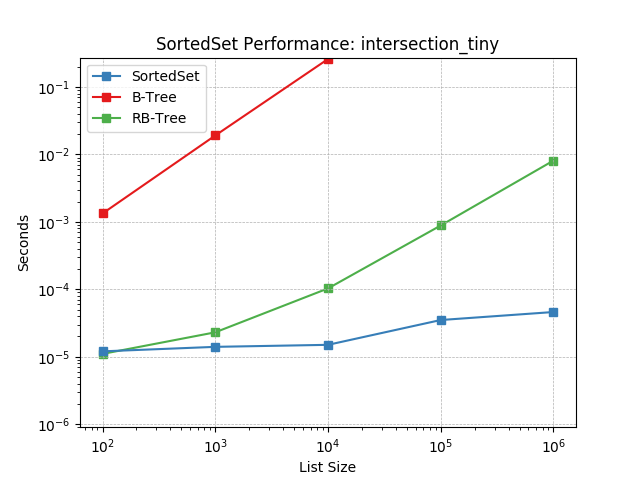
intersection_tiny¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection().
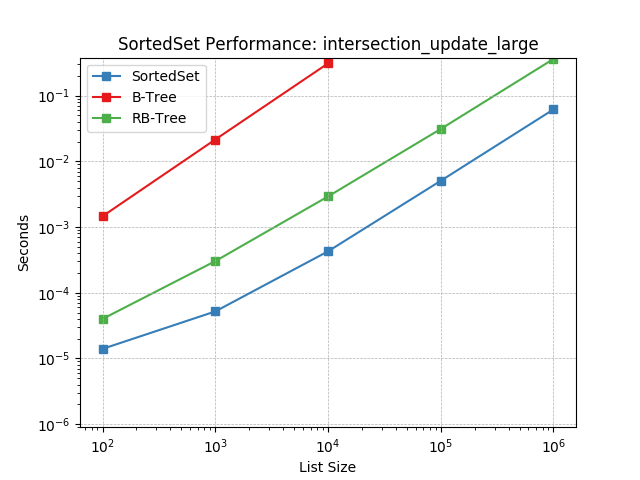
intersection_update_large¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
intersection_update_medium¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
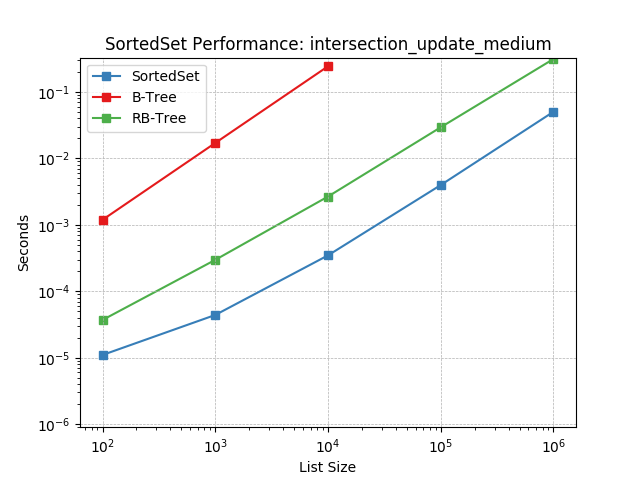
intersection_update_small¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
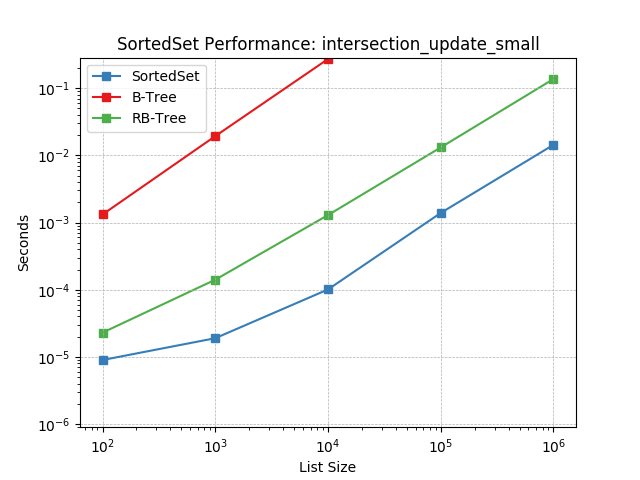
intersection_update_tiny¶
Set intersection using SortedSet.intersection_update().
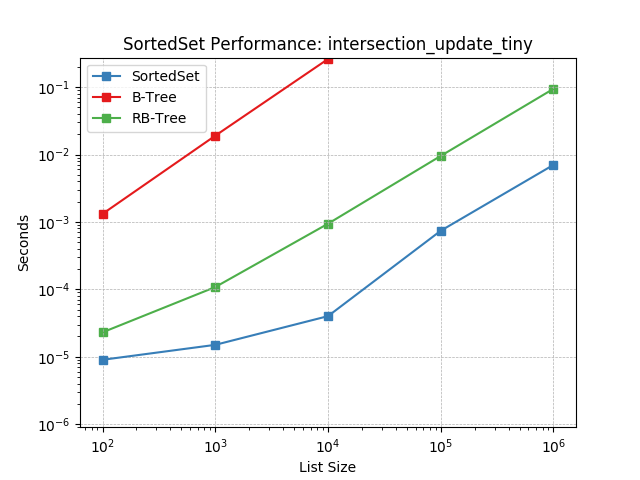
iter¶
Iterating a set using SortedSet.__iter__().
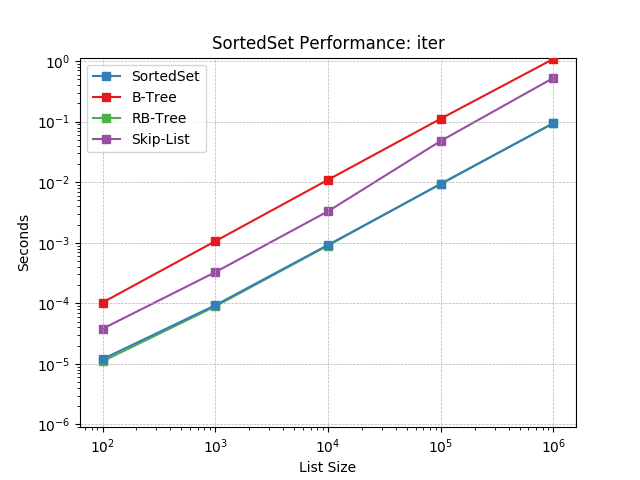
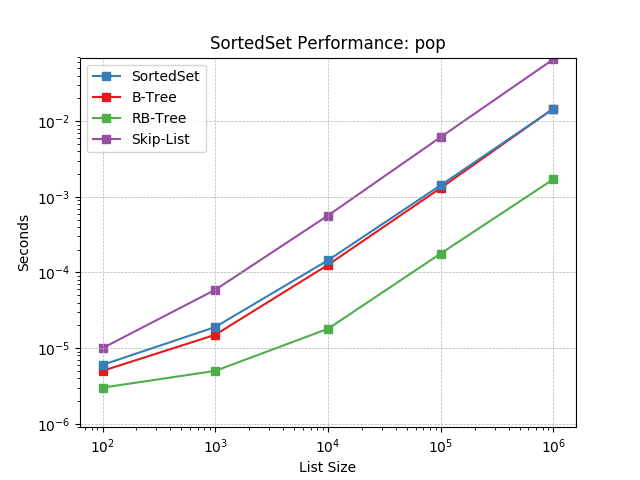
pop¶
Remove the last item in a set using SortedSet.pop().
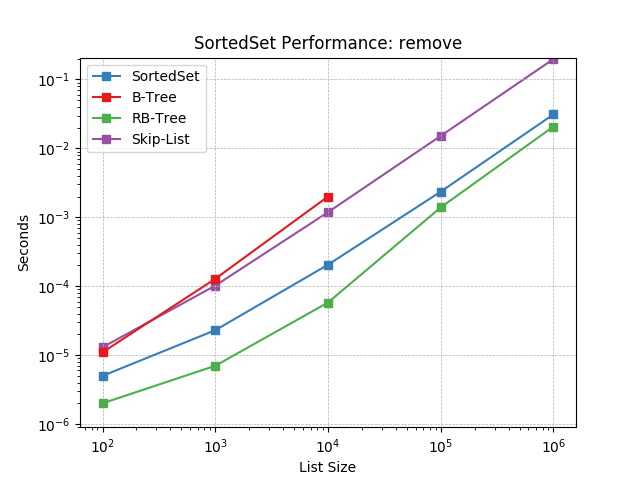
remove¶
Remove an item at random using SortedSet.remove().
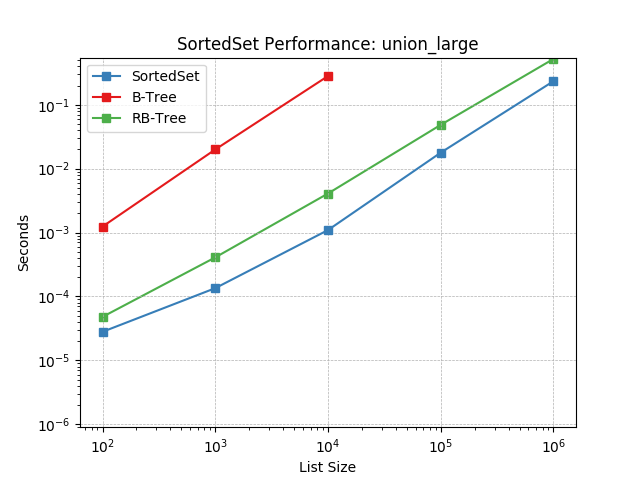
union_large¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
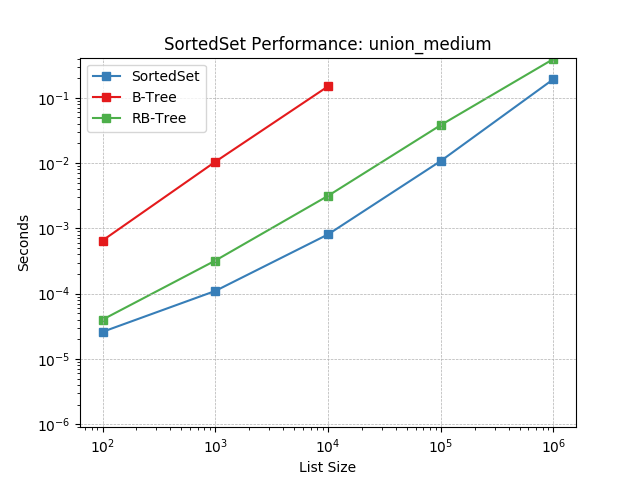
union_medium¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
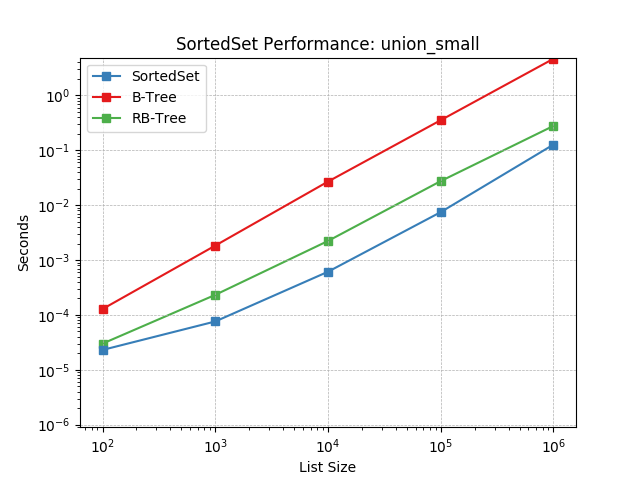
union_small¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
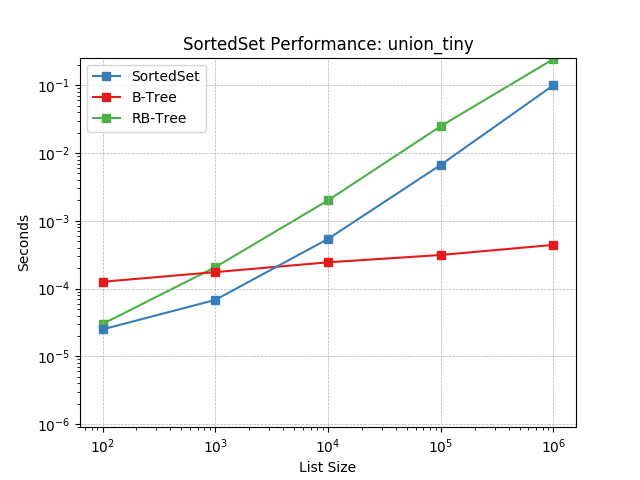
union_tiny¶
Set union using SortedSet.union().
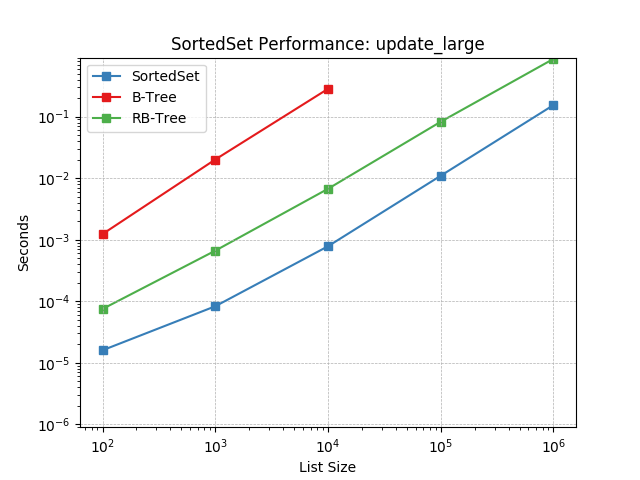
update_large¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
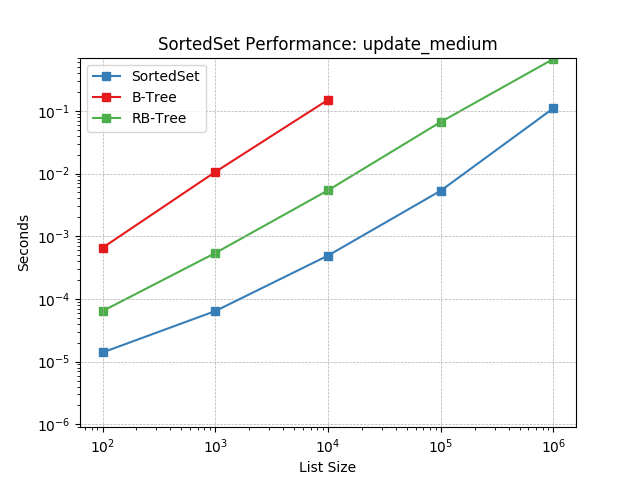
update_medium¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
update_small¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
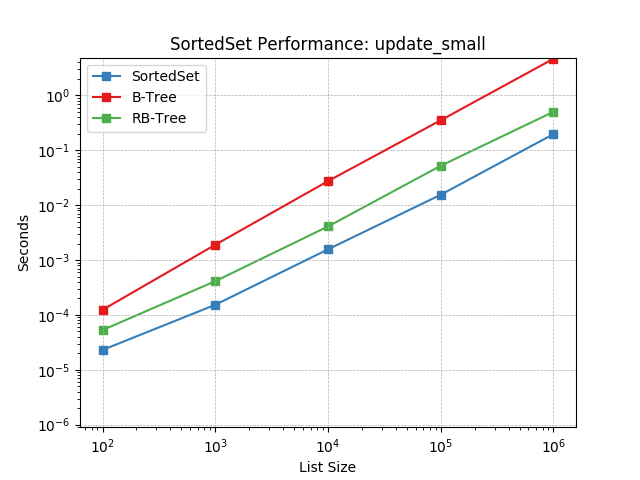
update_tiny¶
Set update using SortedSet.update().
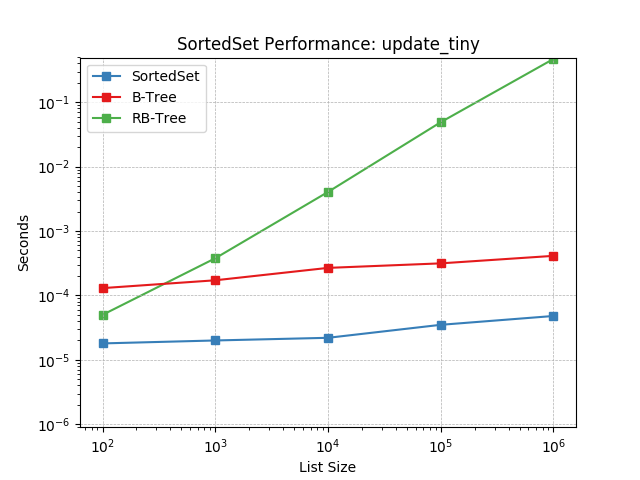
symmetric_difference_large¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
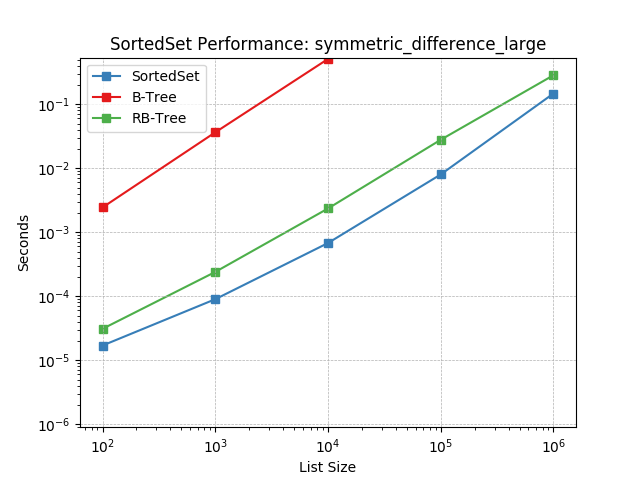
symmetric_difference_medium¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
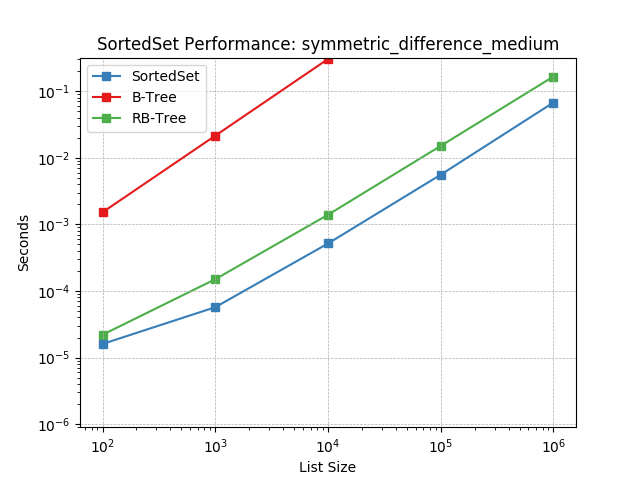
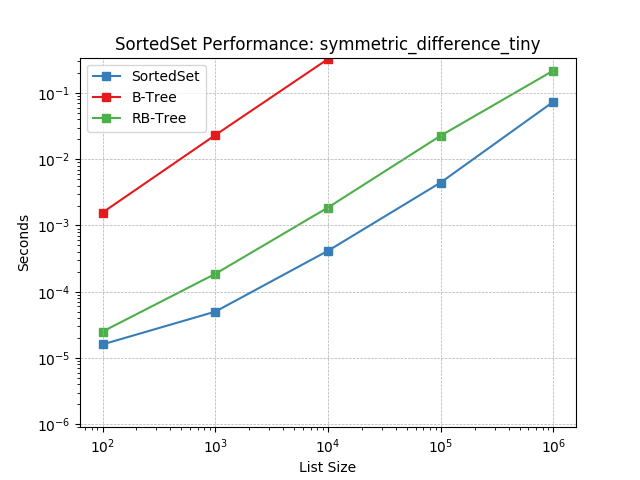
symmetric_difference_small¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
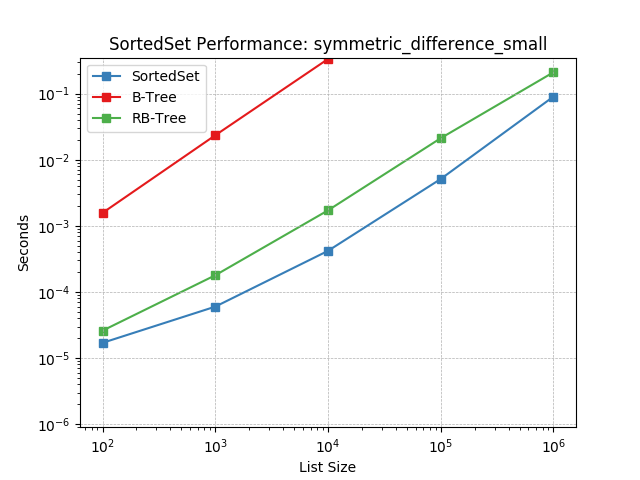
symmetric_difference_tiny¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference().
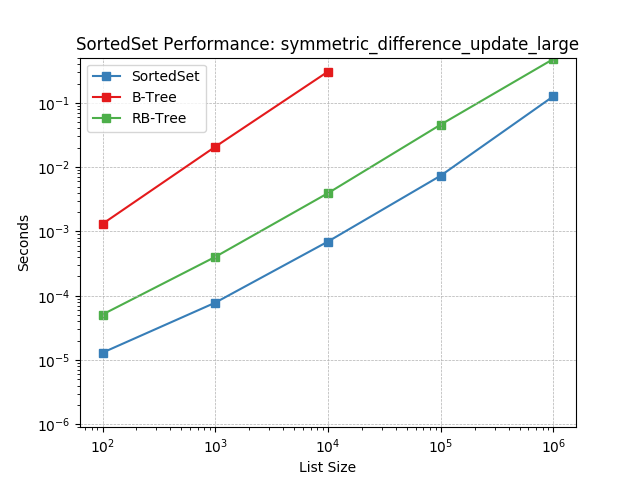
symm_diff_update_large¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().
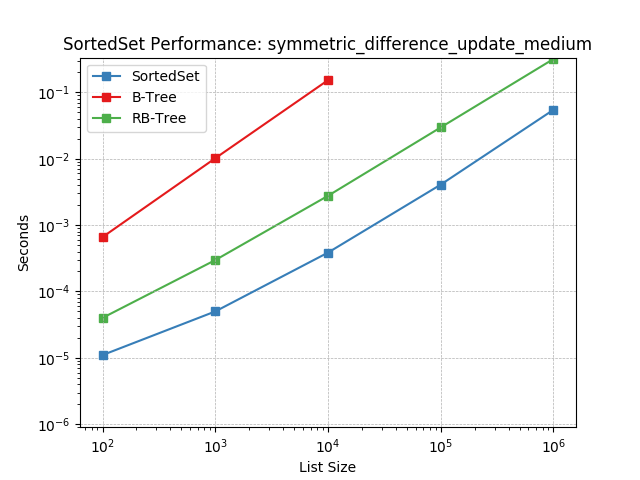
symm_diff_update_medium¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().
symm_diff_update_small¶
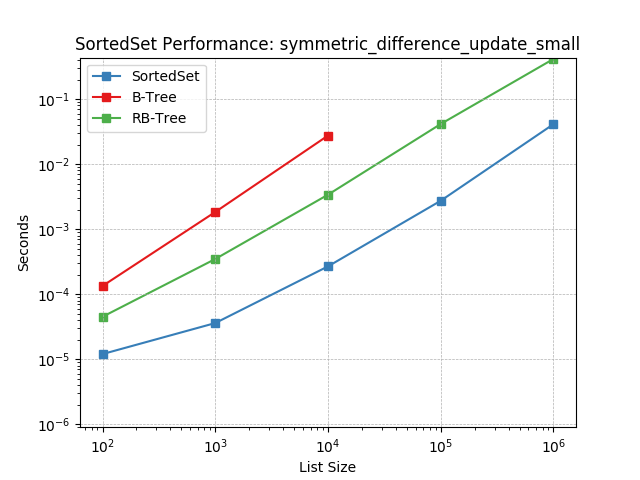
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().
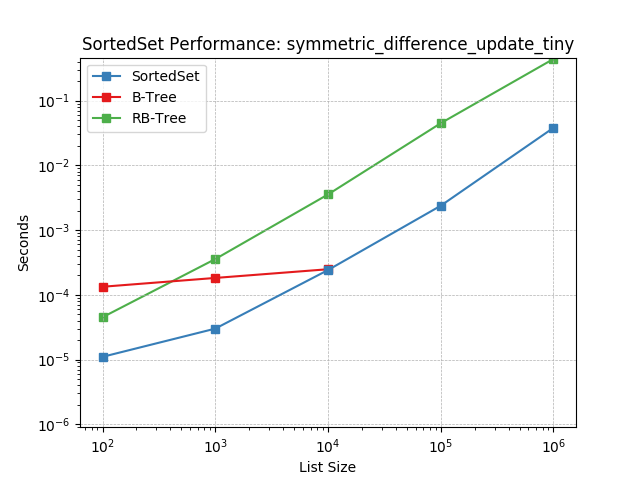
symm_diff_update_tiny¶
Set symmetric-difference using SortedSet.symmetric_difference_update().